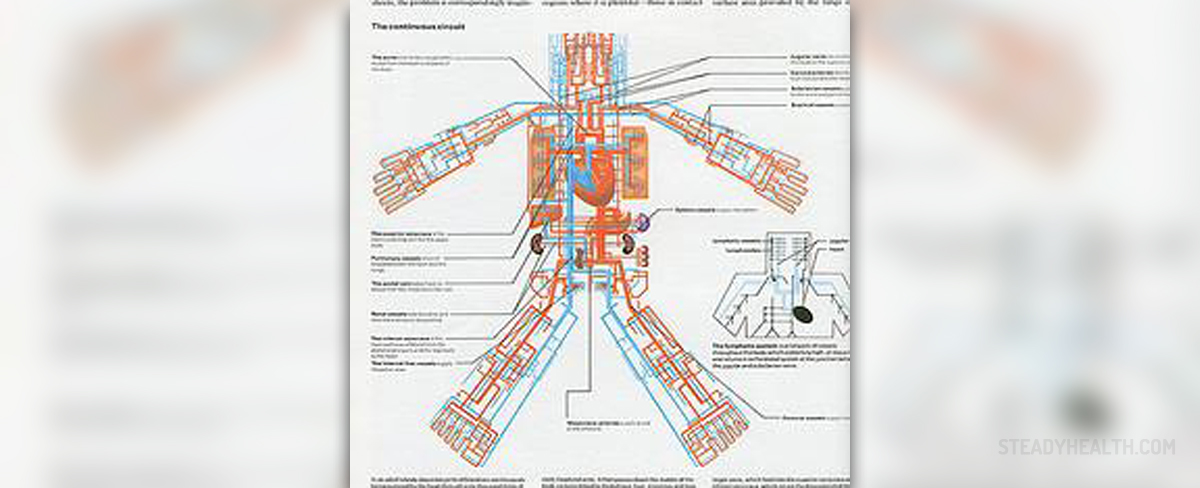
Endocrine system is a system of glands that secretes hormones directly to the blood stream. These hormones are required to regulate various functions of the body, maintain good health and support normal homeostasis. Hormones typically regulate functions such as growth and development of the tissues, function of the tissue, rate at which body burns calories, and even the human mood.
Central nervous system
Hypothalamus is a major part of the brain that controls the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, also known as hypophisis. Hypothalamus releases Thyrotropin-releasing hormone that stimulates thyroid gland; Dopamine that inhibits prolactin released from anterior pituitary; Growth hormone-releasing hormone, that stimulates growth hormone release from anterior pituitary; Somatostatin that inhibits growth hormone and thyroid stimulating horone release; Gonadotropin-releasing hormone, that stimulates follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone release; Corticotropin-releasing hormone that stimulates adrenocorticotropic hormone release, Oxytocin, responsible for uterine contractions and lactation; and Vasopressin, that promotes water re-absorption and increasing blood volume.
Pineal body, also found in the brain and known as epiphysis, releases Melatonin which is involved in regulation of sleep-wake cycle, inducement of drowsiness and lowering of the middle body temperature.Alimentary system
This system has a number of endocrine organs, including stomach, duodenum, liver, pancreas, and kidney.
Stomach releases Gastrin, Gherelin, Neuropeptide Y, Somatostatin, Histamine And Endothelin. These hormones stimulate appetite, secretion of gastric acids, secretion of growth hormone, regulate smooth muscle contractions of stomach, rates of gastric emptying, and suppress release of certain chemicals such as gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin etc.Duodenum produces Secretin and Cholecystokinin. These chemicals stimulate secretion of bicarbonate from liver, pancreas and duodenal Brunner's glands, stop production of gastric juice, release digestive enzymes from pancreas and bile from gallbladder hunger suppressant.Liver produces Insulin-like growth factor, Thrombopoietin, Angiotensinogen and Angiotensin. These chemicals have insulin-like effect, they regulate cell growth and development, stimulate megakaryocytes to produce platelets, and release aldosterone from adrenal cortex dipsogen.
Pancreas secretes Insulin, Glaucagon, Somatostatin and Pancreatic polypeptide. The effects of these hormones are visible on the level of absorption of glucose, glycogenesis and glycolysis in liver and muscle from blood. They also increase blood glucose levels, inhibit release of insulin and glucagon, exocrine secretory action of pancreas and self-regulate pancreas secretion activities.
Kidneys are involved in secretion of Renin, Erythropoietin, Calcitriol and Thrombopoietin. These hormones are involved in activation of renin-angiotensin system by producing angiotensin I of angiotensinogen, stimulation of erythrocyte production, increase in absorption of calcium and phosphate from gastrointestinal tract and kidneys, as well as stimulation of megakaryocytes to produce platelets.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...