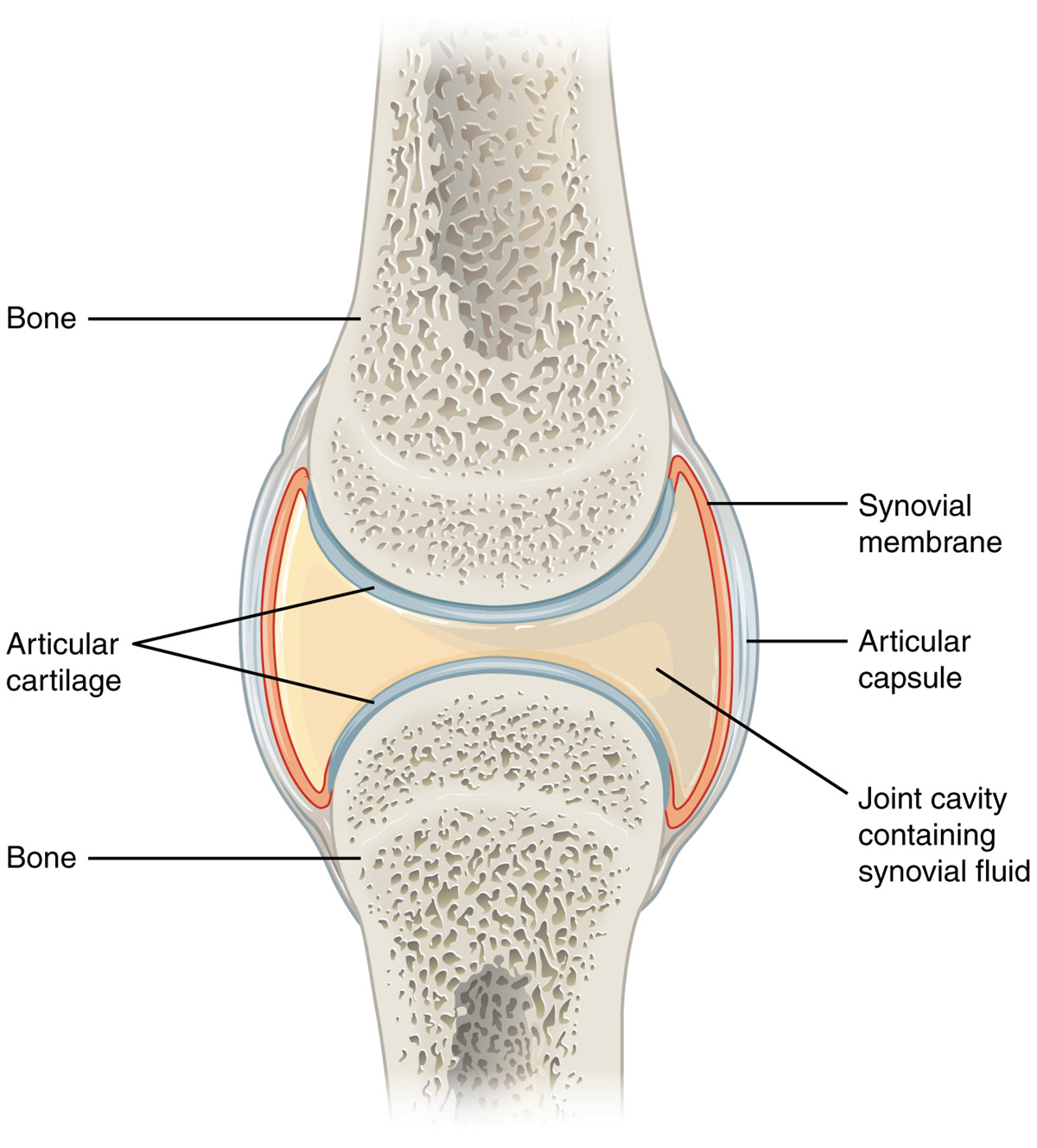
When the synovial or joint lining becomes irritated or inflamed the production of fluid is increased making the joint warm, tender and swollen, and that condition is referred to as synovitis. This joint is encapsulated in membrane tissue called the synovium or the synovial membrane, and it creates a lubricating fluid so the joint is able to move freely and easily. There are many causes of synovitis such as an infection like septic arthritis or tuberculosis, a direct trauma of the joint, some allergic reaction, gout, overuse syndromes or any of the systemic autoimmune inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, and even a rare form of slow-growing benign tumor of the synovial membranes. Synovitis can occur acutely, affecting one or more joints, or it can be a chronic symptom of a more serious illness.
All joints in the body can be affected by synovitis, including hips, knees, elbows, feet, hands and even the joints which connect the skull and the lower jaw. The symptoms of synovitis are related to activity and especially to periods of continuous repetitive movements or a history of physical strains in the past. If the symptoms are not activity-related then other possibilities should be taken into account such as any infections, allergic reactions and inflammations in the recent past because these point to factors underlying the condition. Most often individuals will complain about pain in one or more joints, swelling, warmth or stiffness of the joints in question, with application of heat and cold pads bringing relief. During the physical examination of the joints, the doctor observes the range of motion of the joint to indicate pain, stiffness and possible joint noise. The muscles around the joints are also tested for weakness and pain. The mobility and irritability of the joints is tested as well. The joints will generally feel painful, the movements will be painful and limited, they will also appear swollen, warm and red. There is also a number of laboratory tests involved such as a complete blood count, urinalysis and erythrocyte sedimentation rate to measure the inflammation. A joint fluid analysis can be done if there is a need for it along with an X-ray and a nuclear medicine scan.
The treatment of synovitis consists of controlling the infection and inflammation, reducing the swelling and pain, and then starting the long process of physical therapy, made up of specially designed exercises and the use of ultrasound.








-Arthritis_f_280x120.jpg)


-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)

-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...