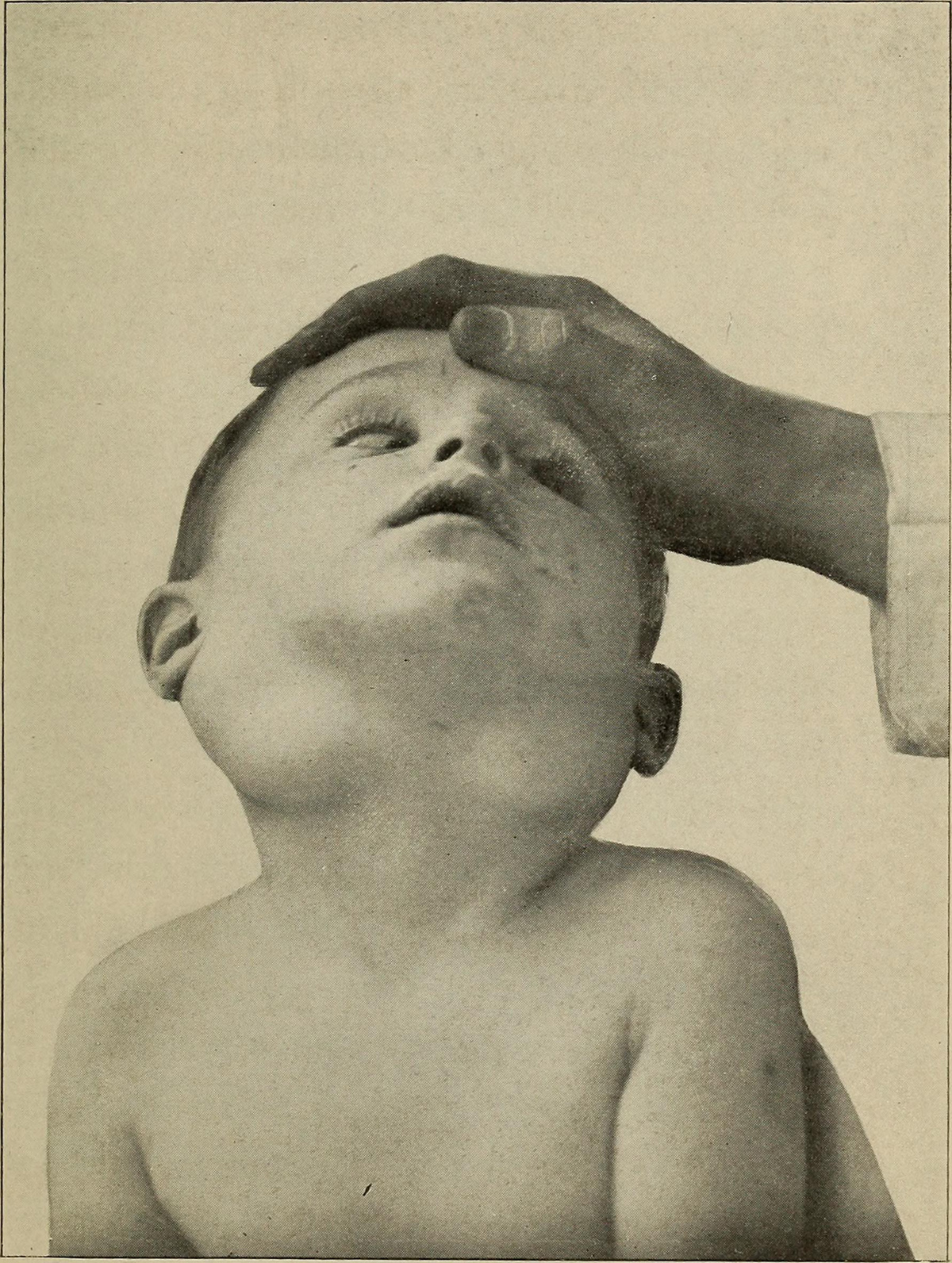
Swollen Adenoids
Adenoids are lymphoid tissue localized at the back of the throat. They include palatine tonsils and adenoids in nasopharynx, the upper part of the throat. These lymphatic structures are in charge with production of antibodies in infants. Adenoids usually become enlarged in case of infections. This particularly refers to chronic infection when they lead to serious problems. Apart from infection, tumors can also lead to enlargement of these lymphatic structures.
The enlargement of adenoids causes pain and problems with swallowing. In infection even fever and chills occur. In children who are suffering from enlarged nasopharyngeal adenoids recurrent ear and throat infection is a standard.
Causes of Swollen Adenoids
Adenoids easily react to infections, both bacterial and viral. These lymphoid structures can also enlarge in hypergammaglobulinemia. Enlarged nasopharyngeal adenoids in children may occur naturally where these structures are large for a child but once the child becomes older and the nasopharynx enlarges these structures do not cause trouble any more. Other option for enlarged adenoids is chronic inflammation.
Symptoms of Swollen Adenoids
Patients who are suffering from swollen adenoids usually have bad breath. Their lips are cracked because they are forced to breath through mouth. This also leads to dry mouth. The problems with breathing are most evident during night. Due to problems with breathing a person even snores. Children also suffer from chronic runny nose and prolonged nasal congestion.
The doctor can set the diagnosis after thorough examination of a patient. He/ she can either look directly into a patient's mouth, or use a special mirror or flexible endoscope to visualize nasopharyngeal adenoids.
Treatment for Swollen Adenoids
Conservative treatment includes antibiotics. They are used in treatment of tonsillitis, enlarged adenoids or sinus infection. Only bacterial infection can be treated with antibiotics. Nasal decongestion is relieved by nasal decongestion drops.
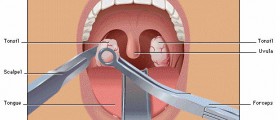
In some children chronic inflammation of adenoids is an indication for operation. Adenoidectomy is performed in children who are suffering from chronic inflammation of adenoids and in patients whose breathing is severely affected by the size of adenoids. Recurrent ear and sinus infections are another indication for adenoidectomy. In some cases adenoidectomy is accompanied by tonsillectomy.
In some patients proper prevention of swollen adenoids can be achieved by timely and appropriate treatment of throat infections.
The surgical removal of adenoids is rather safe and there are several possible complications which include recurrence of ear or sinus infections, bleeding, and a permanent change in child's voice, infections, recurrence of mouth breathing and snoring.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...