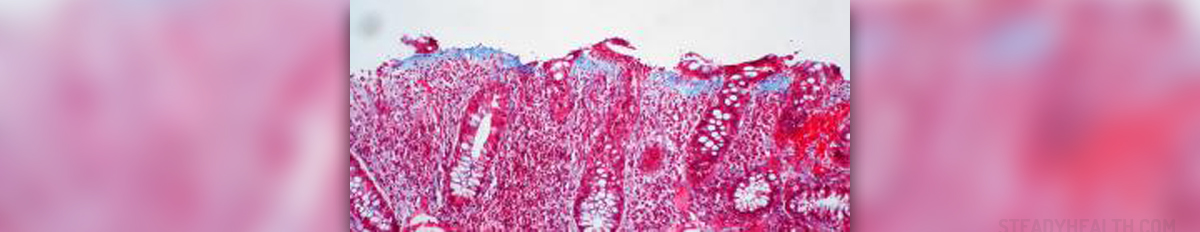
A type of inflammatory bowel disease whichdestroys the large intestine and rectum is called ulcerative colitis. It causespainful swelling and sores in the top layers of the wall of the bowel.This disease is sometimes hard for physiciansto diagnose because symptoms are alike to irritable bowel syndrome and Crohn'sdisease.The cause of ulcerative colitis is still unknown,although researchers believe that virus and bacteria may be potential causes. Ulcerativecolitis is not developed because of emotional strains or certain food products,but these factors may activate symptoms in some people.Risk factors for inflammatory bowel conditioninclude age (people from 15 to 40 years are at higher risk), genetic or family history, immunesystem, infectious agents or environmental toxins, smoking.The symptoms vary in seriousness and may startgradually or unexpectedly. Many factors can result in attacks, includingrespiratory infections or physical stress.Symptoms which may occur are lower abdominaldiscomfort or cramps, diarrhea (blood andmucus may be present), fever, lethargy, food aversion, weight loss, rectal bleeding.Other medical problems that arise involve visionproblems or eye pain, neck or lower back pain, liver disease, osteoporosis,anemia, kidney stones, skin rashes.
Diagnosis
To diagnose ulcerative diagnosis, a detailedphysical examination and a series of tests may be required. In patients who are suspected to haveulcerative colitis, the most significant laboratory studies are stoolexaminations for parasites, stool culture, and testing for clostridiumdifficile toxin to help destroy other causes of chronic diarrhea. A complete blood count may demonstrate anemia fromchronic blood loss. Colonoscopy with biopsy is mostly usedto diagnose ulcerative colitis. Other tests are computerized tomography,x-ray, barium enema.
Procedures
If surgery becomes necessary, the operationpermanently cures ulcerative colitis since the disease only affects the largeintestine and not other areas of the intestinal tract. Surgical procedure iscommon for patients who have colitis that does not respond to complete medicaltherapy, dangerous complications such as rupture of the colon, extreme bleeding,or toxic megacolon, and alterations in the wall of their colon that seem to beprecancerous.There are two surgeries for ulcerative colitisthat cannot be regulated with medications: restorative proctocolectomy andtotal proctocolectomy with ileostomy.This requires the removal of the colon and rectum,creating a small opening in the abdomen, called a stoma, and joining it to theend of the small intestine, called the ileum. Waste will exit the body throughthe stoma, after passing through the small intestine.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...