Pilonidal Cyst - General Information
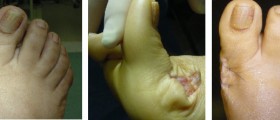
Pilonidal sinus is a chronic infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue that occurs in the furrow between major buttocks muscles, about 2 cm above the anus and spreads upward and toward and on the sides. It is caused by reaction to the hairs that sting in the softened skin of that body part. The disease is four times more often in men than in women. It is more common in obese persons and persons with increased body hairiness. Pilonidal cyst occurs in various forms - from small openings on the skin to the large painful mass. Often appears secretion which may be clear, cloudy or in the form of ichor.
At the beginning of the disease purulent infection (abscess) occurs and after spontaneous or surgical evacuation remains in the form of pilonidal sinus (cavity) under the skin which drains through one or more small openings in the sinus. The pilonidal cavity is usually full of debris mass and body hairs.
If cyst doesn't suppurate, it won't cause particular difficulties, but if it is exposed to frequent contamination, infection is common. In these cases pain occurs, cysts are wider and deeper until they burst and discharge. However, if this cyst is not cured, or if it contaminates again, inflames and creates a very unpleasant symptoms such as pain, difficulties with sitting, walking difficulties, fever, and squeezing pus, etc.).
Indications for Surgery
Acute abscess requires urgent surgical intervention, and chronic sinus produces constant anxiety in patients and it is necessary to be surgically treated.
Pre-operative Tests and Preparation
Diagnosis of pilonidal disease is determined by surgical examination which fulfills with information about the disease provided by the patient.
Acute abscess is usually operated under total anesthesia as an emergency case and surgery for chronic disease conducts under general anesthesia which requires routine anesthetic pre-operative preparation. All chronic pilonidal sinus surgeries may be painlessly carried out under local anesthesia.
If the surgery is performed under general anesthesia there is a ban on eating on the day of surgery, while local anesthesia doesn't require any dietary restrictions.
Surgical Procedure
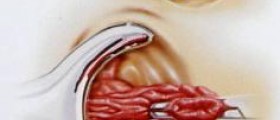
An acute abscess can be removed surgically and discharge abscess collection with irrigation and drainage. Chronic sinus surgery requires cutting out affected area and leaving the wound to heal spontaneously. This procedure has a lower recurrence rate, but requires long-term wound.
Also, there are various surgical techniques of sewing wound. This procedure has a somewhat higher rate of wound infection and subsequent recurrence, but the post -operative period is shorter. Both cases (acute abscess and chronic sinus) requires hospitalization of 1-2 days.
Postoperative Recovery
Postoperative recovery requires regular waxing of the operated region with enhanced hygiene measures. Depending on the surgical technique that was used and the size of the wound, postoperative recovery lasts from ten days to 2-3 months. The patient has no restrictions in food intake after surgery if it is performed under local anesthesia, while after surgery under general anesthesia, food is introduced gradually in the diet (tea, liquid foods, mushy food).









Your thoughts on this
Loading...