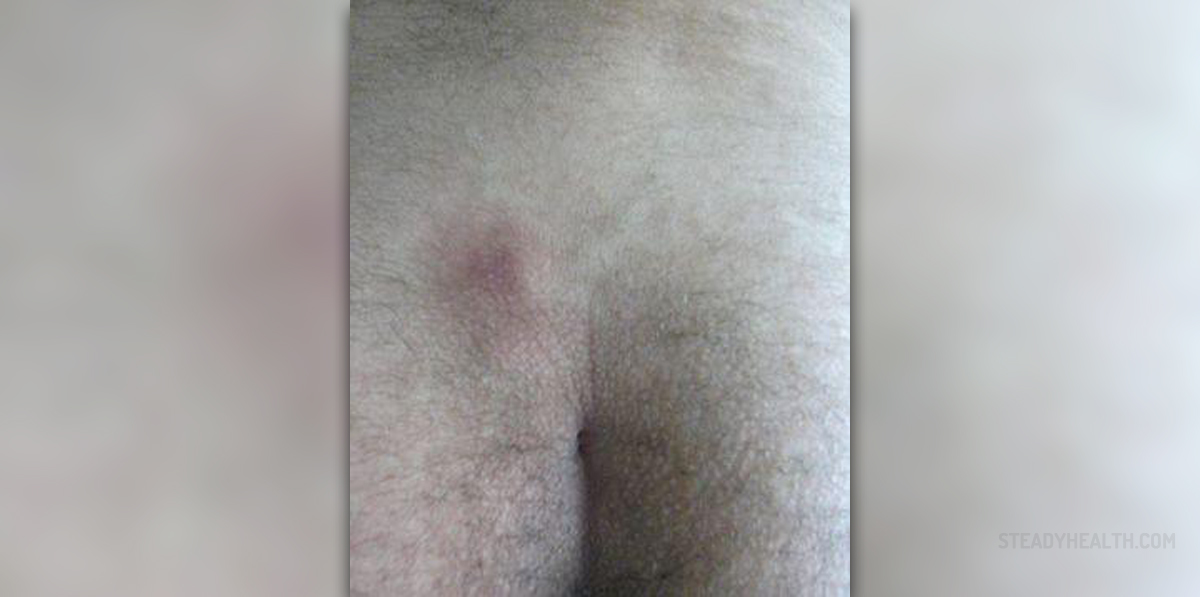
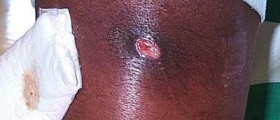
A pilonidal cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms in the skin over the tailbone area. It usually contains hair and skin debris. The word “pilonidal” is derived form the Latin words “pilus” (hair) and “nidus” (nest). Pilonidal cysts are more common in men and usually occur in early adulthood. These cysts are often harmless but if infection occurs, it will result in pain, inflammation and drainage of pus.
The cause of pilonidal cyst is unknown, but most scientists believe it occurs as a response to ingrown hair. People may be susceptible to pilonidal cysts due to excessive pressure or trauma to the sacrococcygeal region.Symptoms of Pilonidal CystsA pilonidal cyst may be asymptomatic and manifest only as a small pit on the surface of the skin at the bottom of the tailbone, near the cleft of the buttocks. However, if the cyst becomes infected it may turn into an acute abscess and several signs and symptoms may develop.
They include redness and warmth of the skin, localized swelling over the lower spine and pain. The pain may be so severe that the affected individual may have difficulty walking and sitting. An opening in the skin may form (a pilonidal sinus) through which pus or blood drains. Sometimes, there may be more than one sinus tract. Also, hair may protrude from a passage below the surface of the skin that connects the abscess to the opening on the surface of the skin. Rarely, infected pilonidal cysts may be accompanied by fever.Treatment for Pilonidal Cysts
Pilonidal cysts with no symptoms do not require any treatment. Infected pilonidal cysts, on the other hand, have to be drained. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. A doctor makes an incision over the affected area and drains the pus. Hair and other debris are then removed and the wound is packed with gauze and left to heal. This treatment is not completely effective and 40% of patients experience recurrence of pilonidal cysts.
For recurrent and complicated pilonidal cysts the treatment involves a more invasive surgical procedure. A surgeon cuts open the cyst to drain it and removes hair and other debris. The wound may be left open and heal form inside out or it may be closed with stitches immediately after the procedure which shortens the healing time but carries greater risk of recurrence. Prevention of Pilonidal Cysts
To prevent formation of pilonidal cysts it is important to maintain good hygiene of the tailbone area. The area must be kept clean and dry and excess hair should be removed with depilatory creams or shaving. Oils and herbal remedies should not be applied to the area. Also, it is recommended to avoid prolonged sitting.
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/pilonidal-sinus/
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007591.htm
- Photo courtesy of GiggsHammouri by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pilonidal_cyst.JPG











Your thoughts on this
Loading...