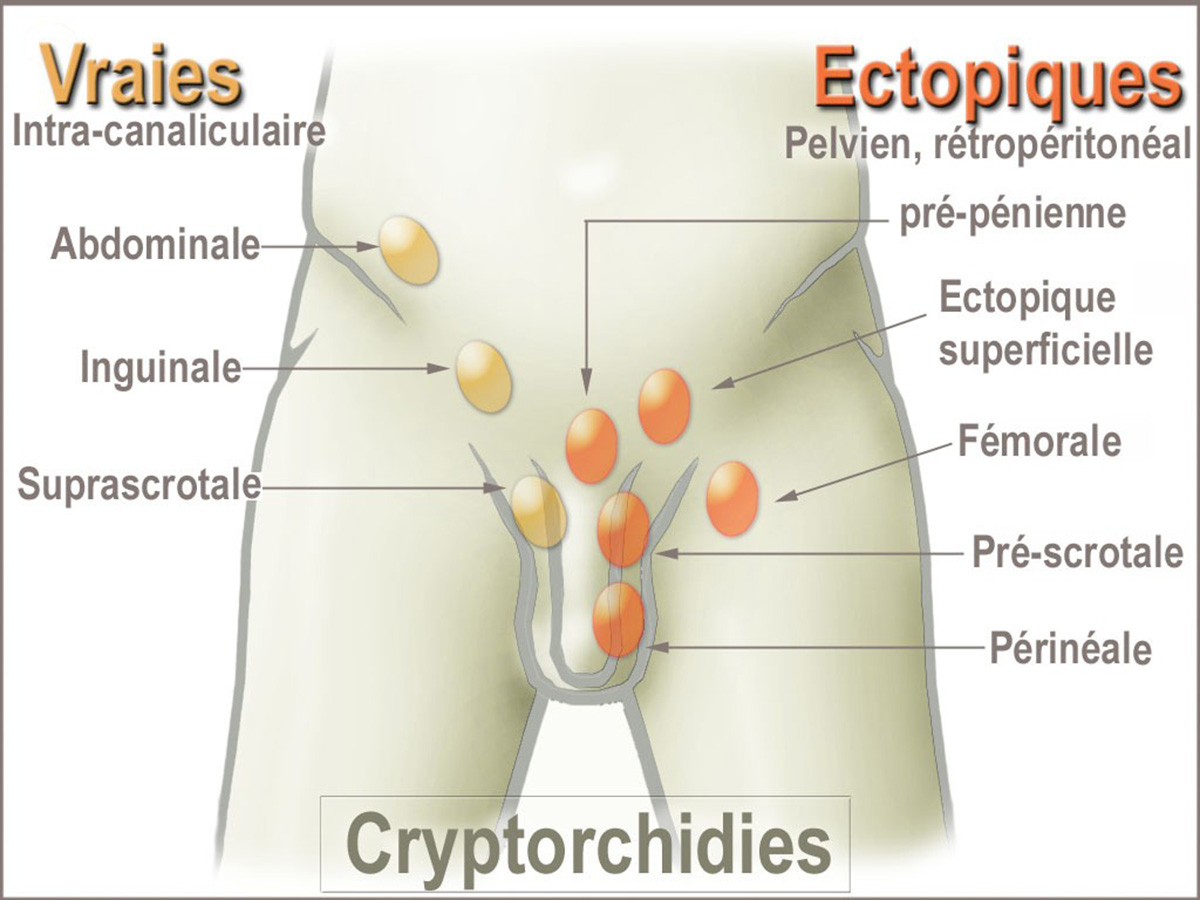
Cryptorchidism is a condition which features with no testicles present in the scrotum. This happens because they did not descend on time during intrauterine development. The condition may affect only one testicle but there are also cases in which both testicles are not placed in the scrotum (testicle sac). Testicles normally develop while the baby is in the womb. They are formed within the abdomen but before the baby is born move down into the scrotum. The state is quite serious and must be surgically treated within the first year of child's life. If not operated condition leads to permanent infertility. This happens because testicles are very sensitive to high temperatures. Within the belly they are exposed to higher temperatures than they are supposed to. In the scrotum the temperature for testicle functioning is optimal. Furthermore the risk of injury to testicles while they are in the abdomen is greater and there is even chance of spontaneous torsion. Additionally the cases of testicular cancer due to cryptorchidism have been reported. Cryptorchidism may develop together with inguinal hernia.
The treatment includes hormonal therapy or surgery. In case of hormonal therapy the patient is administered Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (HCG) the hormone which is in charge with stimulating of testosterone production. The treatment may lead to migration of the testicles into the scrotum.
Before the surgery the child undergoes the thorough examination and preoperative evaluation. Specific laboratory tests together with urine analysis are done. The parents are due to report all the medications the child is taking. Eating or drinking prior the surgery is forbidden for at least 10 to 12 hours. The surgical procedure includes open surgery and Laparoscopic Orchipexy or Orchidopexy. In the first one the testicle is drawn into the scrotum through the inguinal canal and laparoscopic procedure is done in case that the testicle is placed higher in the belly. Both procedures are done under general anesthesia and the patient is discharged the same day.
Pain and discomfort are side effects of the surgery and are relieved with pain killers. The surgical stitches will dissolve spontaneously without any need to be removed by the surgeon. Bruising and edema of the scrotal area are normal side effect and they will reduce slowly in few days.
The child who has undergone this kind of procedure goes to regular check-ups once a year. This is done to make sure that the testicles are developing properly. Additionally after reaching the adolescence the patient will be taught how to examine his testicles in order to notice potentially newly formed lumps. This self-examination is supposed to be done every month.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...