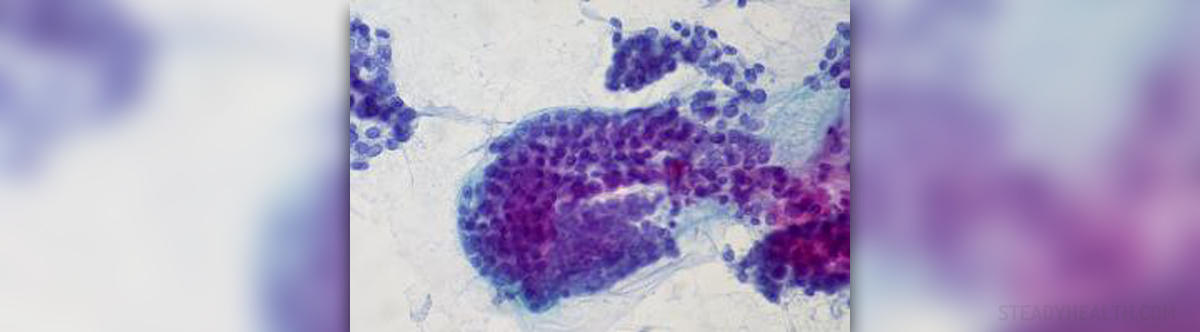
Thyroid Cancer - Introduction
Thyroid cancer is a malignant tumor of the thyroid gland. Each year an approximately 37.00 new cases of thyroid cancer are reported in the United States. This cancer affects both genders and may occur at any age. Still, it predominantly affects people older than 30. The tumor is most commonly in a form of a nodule which does not cause any symptoms. If there are symptoms they usually include hoarseness, neck pain or enlarged cervical lymph nodes (progression of the disease).
There are 4 patophystological types of thyroid cancer. They include papillary cancer, follicular cancer, medullary cancer and anaplastic thyroid cancer. There is even a chance of a combination of these cancers so some patients may suffer from a combination of papillary and follicular thyroid cancer. The most common type is papillary cancer. The most malignant one is anaplastic cancer which may progress rapidly and spread even in early stage of the disease.
Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer may be asymptomatic. This can delay setting of the diagnosis and treatment. Thyroid cancer is usually in a form of nodule. Luckily majority of thyroid nodules are not malignant.
In many patients the presence of nodule in the thyroid gland drives them to see their doctors. This lump requires further examination and certain tests. Sometime the nodule is not visible but can be palpated. Well experienced doctors can palpate even the smallest lump. This can be explained by the fact that under normal circumstance the thyroid gland is not palpable so any kind of growth can be easily detected.
One more sign of thyroid cancer is enlargement of cervical lymph nodes. Not all the thyroid cancers will spread to the regional lymphatics. This usually occurs in anaplastic thyroid cancer and advanced stages of other pathohystological types.
Hoarse voice is another possible sign of the presence of thyroid cancer. Hoarseness occurs due to infiltration of the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
In case of large nodes one may experience problems with swallowing and breathing is usually jeopardized only if the tumor is rather large or infiltrates and compresses the trachea.
And finally, in rare occasions thyroid cancer may be a cause of the neck and throat pain.
Prognosis of Thyroid Cancer
Fortunately, majority of thyroid cancers are curable. The therapy is most effective in case of papillary and follicular cancers which are the most frequent types of thyroid cancer. The treatment for these two pathohistological types includes surgical resection of the tumor and sometimes postoperative application of radioactive iodine.
Medullary thyroid carcinoma has worse prognosis since it tends to spread to regional lymph nodes in early stage of the disease. This type is treated with surgical resection of the tumor and regional lymph nodes. Radioactive iodine is not administered in patients with this cancer since medullar thyroid cancer does not bind radioactive iodine.
And finally, the worst prognosis has anaplastic thyroid cancer. It spreads to regional lymph nodes or even distant organs rather early. Depending of the stage and what organs has been affected anaplastic thyroid cancer requires more aggressive treatment comparing to other types.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...