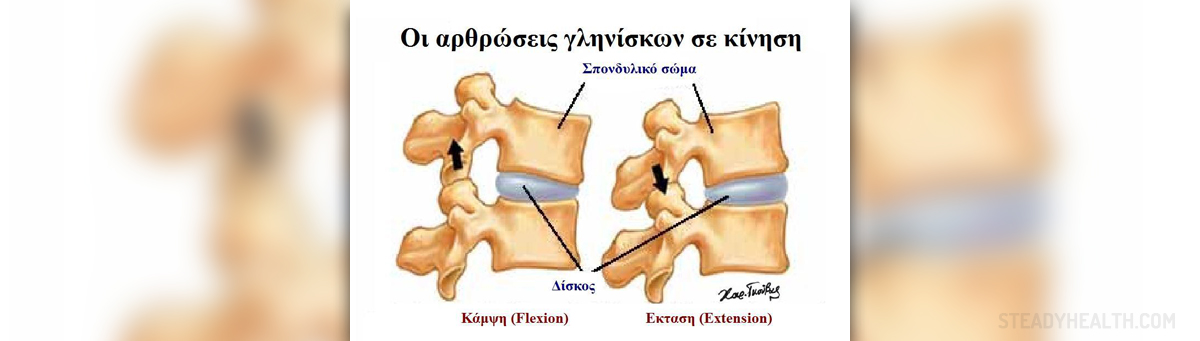
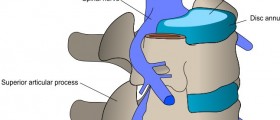
The facet joints represent connection between the vertebrae. In humans there are 24 vertebrae. Each of them is connected with two facet joints with the upper and the lower vertebrae. Around facet joints there is a thick bunch or capsule of ligaments. The capsule is lubricated with synovial fluid. There is a layer of smooth cartilage between the two facet joints.
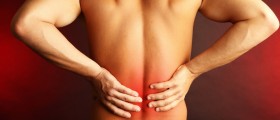
Joint disease that affects facet joins is known as facet arthropathy. This is a serious, painful and disabling condition. Depending of the portion of the spine that is affected there are cervical, thoracic and lumbar facet arthropathies.
It cannot be said for sure how often this arthropathy affects people. Some studies have shown that less than 10% of all patients suffering from low back pain are actually suffering from lumbar facet arthropathy. The research regarding neck facet arthropathy is even less available. It seems that facet arthropathy affects people older than the age of 50 and that it is equally frequent among both genders.
Symptoms and Signs of Facet Arthropathy
Even though the symptoms and signs of facet arthropathy resemble symptoms caused by other conditions of the spinal column there is a slight difference. Namely, the pain in facet arthropathy tends to become more intensive on one side of the spinal column. Furthermore, it may radiate towards the upper or lower extremities. If this is the case the arms and legs may additionally be weak and numb. Cervical facet arthropathy may induce headache and severe neck pain.
Diagnosing Facet Arthropathy
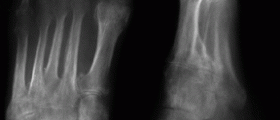
The doctor investigates patient's medical history and performs additional tests and examinations such as an x ray of the spinal column, MRI of the spine and imaging tests that can confirm or rule out degenerative changes in the joints. Sometimes there may be discrepancy and patients with severe pain may not have so intensive degenerative changes while others can have significant degenerative changes while experiencing no pain or low intensity pain.
Treatment Options for Facet Arthropathy
Many patients can benefit from physical therapy. This is the most significant part of the treatment from facet arthropathy. The range of motions in the affected joints is increased, the muscles strengthened and ligaments start to provide with more support.
Pain caused by facet arthropathy can be alleviated with acetaminophen and ibuprofen. In case of more intensive pain patients may be prescribed weak opoids such as tramadol or codeine. If there is a nerve irritation it is treated with tricyclic antidepressants, gabapentin, pregalabin or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors. In case pain becomes unbearable it is alleviated with strong opoids like morphine.
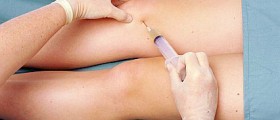
Injections of local anesthetics into the facet joints are more used in diagnosing facet arthropathy than in the treatment. Injections of corticosteroids can prolong effects achieved by local anesthetics. It may be possible to disrupt the nerve innervating the facet joint. The effects are short-lived and the treatment must be repeated after 6-9 months.








Your thoughts on this
Loading...