Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are definitely the most significant class of antidepressants prescribed during the recent years. In the United States there are six of such medications including citalopram (Celexa), escitalopram (Lexapro), fluoxetine (Prozac), fluvoxamine (Luvox), paroxetine (Paxil) and sertraline (Zoloft).
These medications are prescribed to the patients suffering from unipolar and bipolar major depression and anxiety disorders. Some studies have shown the efficacy of the previously mentioned drugs in treating other conditions such as dysthymia, premenstrual dysphoria, bulimia nervosa, obesity, borderline personality disorder, alcoholism, rheumatic pain and migraines.
Among members of SSRI class of medications there are similarities as well as differences. All these medications have the same mechanism of activity but there are slightly different pharmacological and pharmacokinetic characteristics.
Mechanism of Action of SSRIs
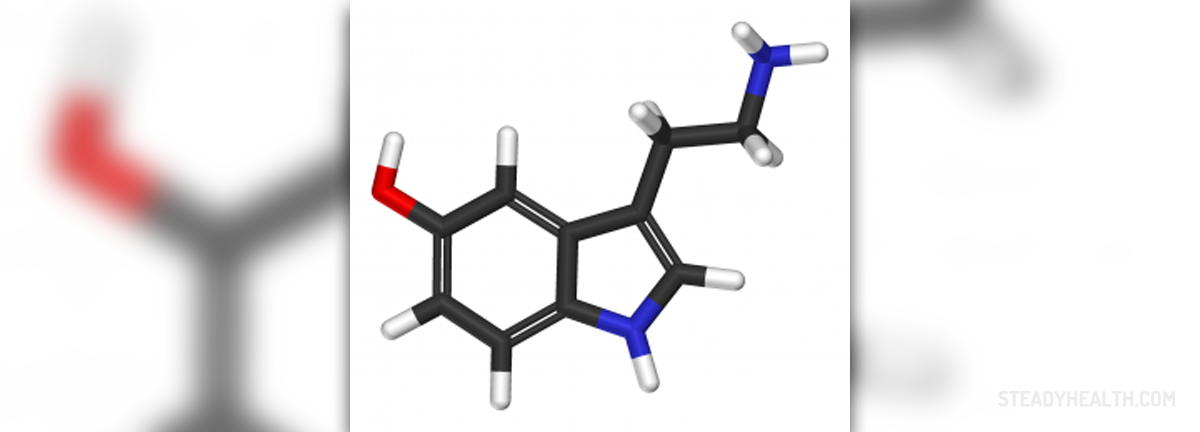
Serotonin is one of the brain's neurotransmitters. Norepinephrine is another one although there are several more of brain's neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are substances that carry signals between brain cells. In case the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine are low this does not point to depression but if they are artificially increased patients suffering from depression may feel improvement of symptoms and signs of this disorder. SSRIs block the reabsorption (reuptake) of serotonin, hence allowing for more serotonin to be available. This consequently enhances neurotransmission and improves mood.
Side Effects of SSRIs
There are several side effects of SSRIs. They are generally mild to moderate and almost never require a dose reduction or discontinuation.
Nausea is the most common side effect of SSRIs. This particularly refers to paroxetine and sertraline. In some cases patients also complain about diarrhea. One more side effect is sexual dysfunction. It may be associated with the disorder itself or develop as a result of the therapy. Fluoxetine is the drug that in minority of cases leads to sexual dysfunction.
Anticholinergic effects are most prominent if patients are prescribed with paroxetine. These effects include dry mouth, constipation and cognitive disruption. Some of SSRIs may cause weight gain (particularly paroxetine) while others may induce weight loss (initial phase of treatment with sertraline). Fluoxetine acts appetite-suppressive if administered for a short period of time.
Fluoxetine is most potent when it comes to anxiety and agitation as potential side effects while escitalopram and paroxetine may cause insomnia but not as often as fluoxetine or sertraline. Paroxetine is associated with drowsiness, fatigue and somnolence. And finally, sertraline and fluoxetine cause headache more than other SSRIs.
Drug Interactions
It is essential never to combine SSRIs and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Such combination leads to a hyperserotonergic syndrome (excitement, diaphoresis, rigidity, hyperthermia, tachycardia, hypertension and in some cases death). A combination of thioridazine and paroxetine or fluoxetine may cause serious heart problems. SSRIs with the lowest potential for drug interactions include citalopram, escitalopram and sertraline.


_f_280x120.jpg)












Your thoughts on this
Loading...