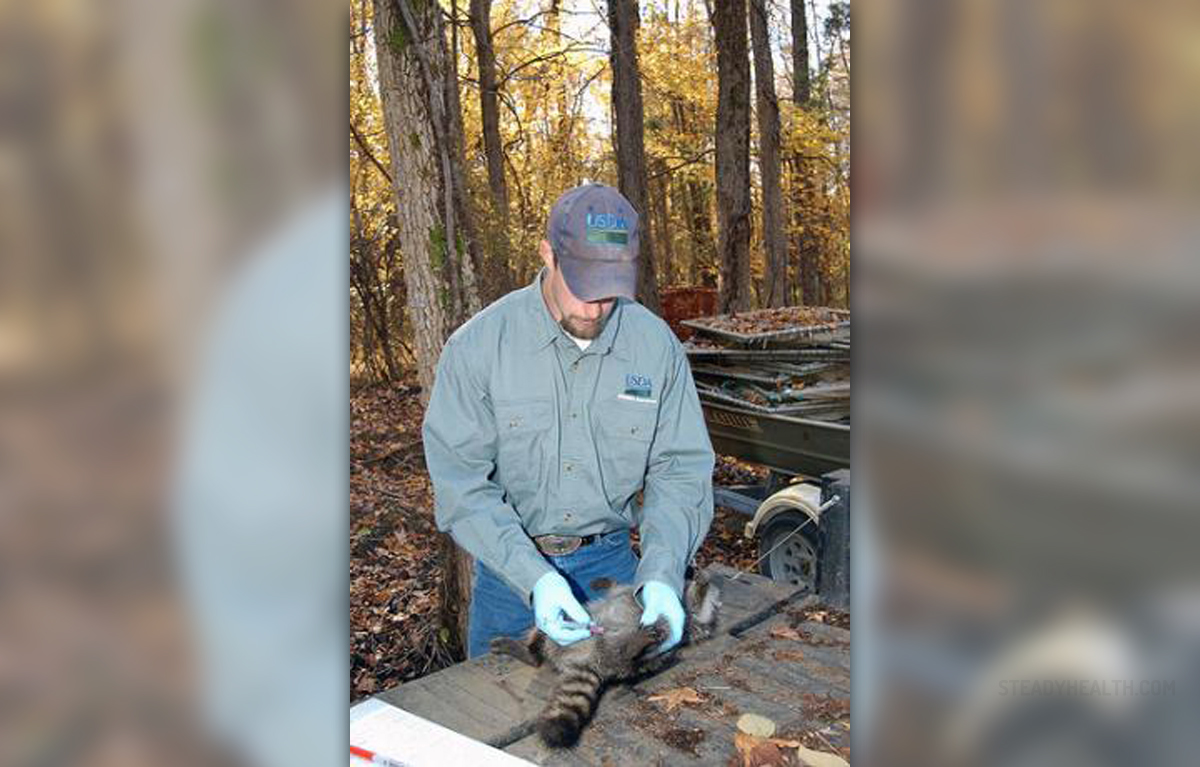

Rabies is a viral disease that affects warm blooded animals but can be transmitted to humans usually through animal bites.
Symptoms of rabies
Symptoms of this disease can start anytime between two weeks and two years after the contraction, although it commonly takes two to twelve weeks for their onset to take place. First it starts with symptoms similar to a common flu but if it progresses, paralysis, cerebral dysfunction, anxiety, seizures and hallucinations can be expected.
If not treated with post-exposure medicines, rabies can be fatal.
Rabies vaccine
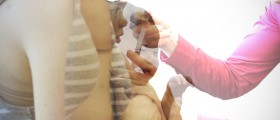
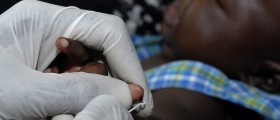
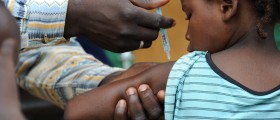
Rabies can be prevented by vaccination in most humans and animals. In most countries vaccination is obligatory for pets, especially dogs.
Any healthy person can get vaccinated, even persons with a minor illness for example people who have a cold. Other moderately severe or severe illnesses, require waiting for a full recovery before the vaccine is administered. However if a person has been exposed to the rabies virus, he or she should be vaccinated regardless of any disease or condition they might have.
Some professions are considered to carry a higher risk of contracting rabies, such as veterinarians, employees at zoos and national parks, spelunkers, laboratory workers and similar occupations.
Before taking a rabies vaccine, people who have HIV/AIDS, receive treatment for cancer like radiation or chemotherapy, drugs for malaria or drugs for immune system, should inform their doctor about it. The same goes for pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Side effects of the rabies vaccine
In most cases when a side effect is reported, it is related to dermal reactions at the injection site, like pain, itching, edema or limb swelling. Systemic reactions, if they occur, usually includes dizziness, fatigue and headache and are generally similar to flu symptoms. These side effects do not require a cessation of immunization and the boosters may be administered.
The vaccination should be discontinued in case the patient has an anaphylactic or neuroparalytic reaction.
Cardiovascular side effects may includes a fast pulse and flushing, and as for the effects on gastrointestinal system, there may be some nausea and vomiting.
Hypersensitivity, or an undesired reaction by the immune system, in case of rabies vaccine may include anaphylaxis, urticaria and pruritus, bronchospasm and edema.
More serious and potentially dangerous side effects are related to the nervous system. The reactions may include fatigue and dizziness, but also encephalitis, meningitis, Guillain-Barre syndrome, neuroparalysis, multiple sclerosis and others.
These side effects are usually and effectively, treated with corticosteriods but this treatment may inhibit the effects of the immunization for rabies.






Your thoughts on this
Loading...