Pituitary tumors larger than 19 millimeters are known as macroadenomas. These tumors can cause physical pressure on the pituitary gland and other nearby structures. Biochemical and physical problems can occur as a result of these tumors.
Symptoms and types of tumor
If one is suffering from the onset of a pituitary tumor, one might experience symptoms that include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, weakness, loss of vision, headache, low blood pressure, hair loss, sexual dysfunction and unintended weight gain or weight loss.
Some tumors - known as functioning tumors - will lead to the production of hormones. This will lead to an overproduction of hormones, which can lead to the occurrence of various biochemical effects. There are different types of these tumors that exist, with their own specific symptoms. Adrenocorticotropic hormone-secreting (ACTH) tumors, for example, stimulate the hormone adrenocorticotropin, and can lead to fat accumulation, facial roundness, a hump on the upper back, hypotension, muscle weakness, bruising, stretch marks and a thinning of the skin.
Some tumors lead to a secretion of the growth hormone. These tumors can lead to a coarsening of the facial features, enlarged hands and feet, excessive sweat produce, hypotension, heart problems, malocclusion and degenerative arthritis. Gigantism can also occur in children and adolescents.
Other tumors secrete prolactin. These tumors can lead to decreased sexual hormone production in both sexes. However, some differences do exist between the sexes. For females, oligomenorrhea, amenorrhea and galactorrhea can occur. With men, erectile dysfunction, infertility, hair loss, loss of sex drive and gynecomastia can all be symptoms of this type of tumor.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone secreting tumors can lead to an overproduction of thyroxine and thus sudden weight loss, rapid or irregular heartbeat and nervousness or irritability. If you have symptoms similar to any that were detailed above, you should consult a doctor, particularly if you have a family history of similar conditions.
Treatment
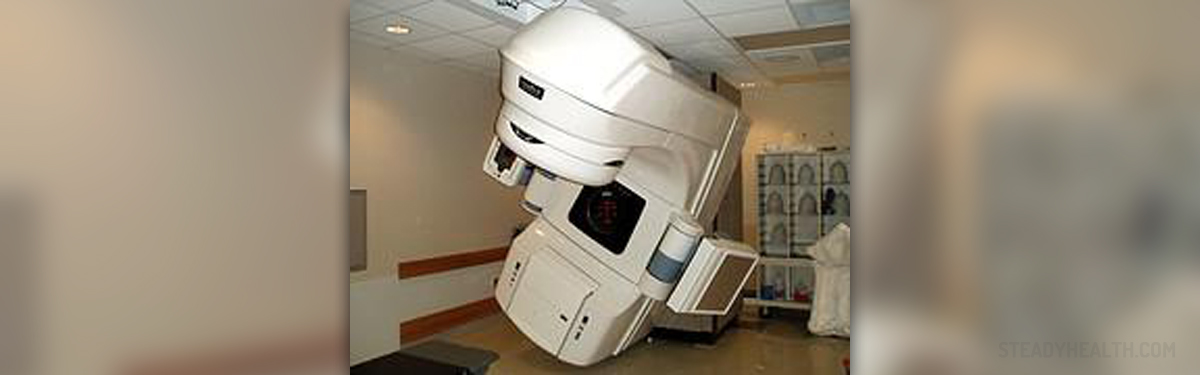
Treatment will depend on the type and size of the tumor. Other factors, such as overall health and age will also play a part in deciding the approach to treatment. Treatment might require neurosurgery, radiation therapy and associated medications. The treatment team might include a neurosurgeon, endocrinologist and a neurologist. Surgery will be a necessity if the tumor is pressing on the optic nerves or if the tumor is producing too many hormones. Radiation therapy employs the use of x-rays to destroy the tumors. This can be used separately to or in conjunction with surgery.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...