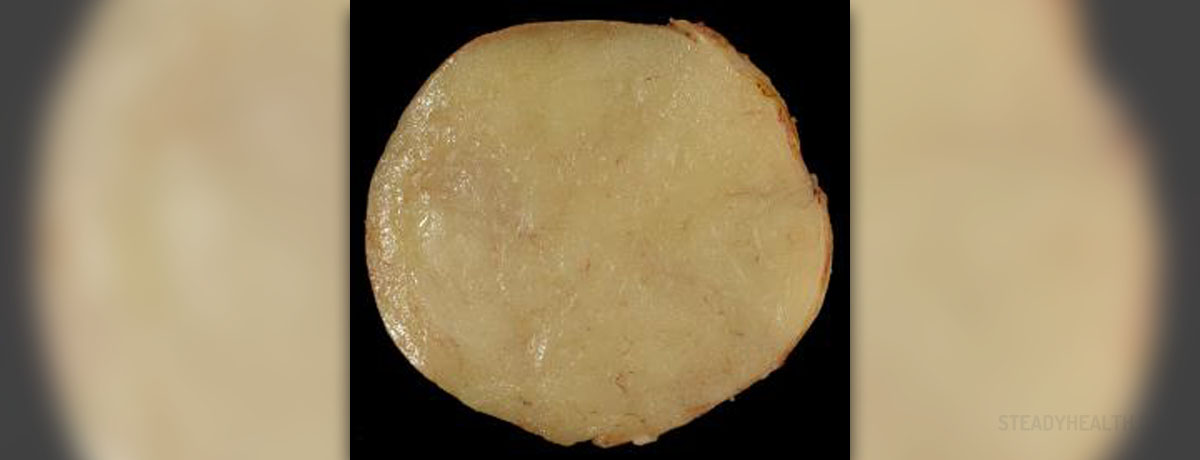
Lipoma
Lipoma is the term used for the incidence of a small fatty lump that forms between the skin and the underlying muscle layer. Of all the benign tumors, lipomas are the most common and the most frequent. These non-cancerous tumors can be found in the subcutaneous tissues and in internal organs, but very rarely. They appear as distinct hard masses in the subcutaneous tissues of the chest, and typically they are several centimeters in size. A surgical excision or liposuction is necessary for their removal.
The majority of single cutaneous lipomas shows clonal alterations, while multiple lipomas do not show these alterations. The real cause for the occurrence of lipomas is not discovered yet, although many researchers are doing their best to establish it. However, there are some clues that lipomas are inherited condition and that certain genes are responsible for that. Lipomas are not very serious condition and it is not dangerous or life-threatening disorder. The adverse effects of lipomas are just mild tenderness. Furthermore, solitary lipomas are more likely to appear in women than in men, whereas multiple lipomas more frequently appear in men. Lipoma is not a condition characteristic for children and infants. Usually it occurs in early adulthood, although it may appear at any age.
Treatment of lipomas
For treating lipomas many doctors practice mesotherapy. Mesotherapy is a kind of treatment that includes a series of injections which contain vasodilators, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, enzymes, or hormones. To treat lipomas a lipolytic agent called lecithin with deoxycholate is used. Surgical care is always more preferable than medical care when lipomas are in the question. There are many surgeries that are very effective in lipomas removal. Lipomas may infiltrate even into intramuscular or intermuscular locations, as well as into bone, tendon, or nerve, and because of this careful microdissection is necessary in order to preserve important structures.
For a simple surgical excision of lipomas, first of all, the clear borders on the skin must be marked before infiltrating with anesthesia. The next step is to incise the skin down to the lipoma membrane and free the lipoma from the surrounding tissue. When hemostatis is achieved, the dead space must be closed as well as the wound. To avoid hematoma or formation of seroma, a pressure dressing must be applied for the next 24 hours. The best and easiest way to get rid of lipomas is liposuction, because it is completed in the optimal time and the incisions are very small. Furthermore, liposuction is the most recommended method for the treatment of lipomas by many specialists.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...