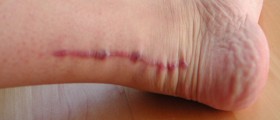
Plantar fascia is a band of fibrous tissue that runs along the bottom side of the foot. Its role is to support the arch of the foot. When it becomes inflamed, it causes a condition called plantar fasciitis. The plantar fascia can also suffer from a tear or a rupture. It can occur due to abnormal foot mechanics, strenuous activity related to the foot and several other causes. Whatever the reason is, ruptured plantar fascia should be treated as soon as possible. As for the symptoms, the most prominent one is pain, especially in the heel, and also redness, swelling, bruising and tenderness at the soles of the feet.
Causes of plantar fascia rupture
One of the most common causes of problems with plantar fascia is the overuse of the ligament. This can happen because the footwear is fitting well, if a person is obese and puts too much pressure to the feet, if the fascia is exposed to too much strain during physical activities, certain biomechanical abnormalities and inadequacies and similar issues.
Flat feet are another factor that may lead to inflammation, tears or ruptures of plantar fascia. Fat pad atrophy, a condition in which the fat pad that covers and protects the fascia gets worn out, can also lead to plantar fascia rupture.
Treatment for plantar fascia rupture
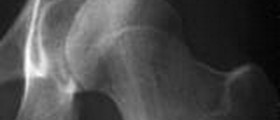
A ligament tear in any part of the body is a serious matter and requires medical evaluation. If the symptoms of plantar fasciitis or rupture appear in form of pain, redness and swelling, it is best to see a doctor. Doctors can make a rather precise diagnose of plantar fasciitis rupture based only on the symptoms and the physical exam, but they usually order some X-ray images to be sure.
As for the treatment, the RICE approach, which stands for rest, ice, compression and elevation, used for almost all ligament injuries, is the best course of treatment for plantar fascia rupture. This approach greatly reduces the symptoms and promotes healing and recovery.
Pain killers can be taken to alleviate the pain and if the pain is very severe, corticosteroid injections may help.
Once the symptoms subside, it is recommended to do regular plantar fascia stretches. These, however, should not be done without the supervision of a physical therapist or a similar professional. It is also recommended to see a podiatrist who will advise the patient on the types of footwear that reduce the chance of recurring ruptures.
If no treatment works and the symptoms persist for more than nine months, it may be necessary to perform a surgery to fix the rupture. This, however, does not happen very often.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...