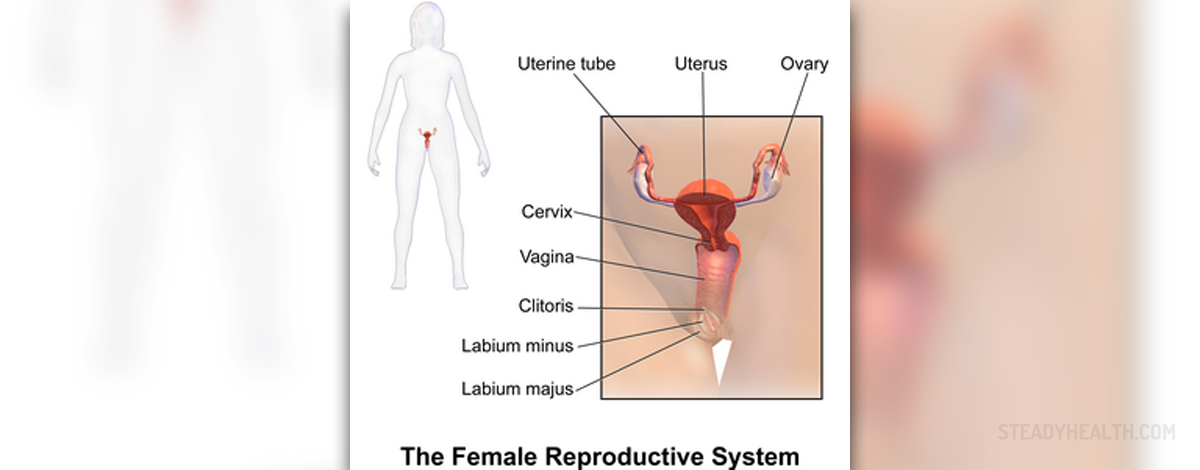
The fallopian tube connects the ovaries to the uterus and is responsible for egg transportation. If a woman becomes pregnant and the egg does not leave the fallopian tubes, it can result in an ectopic pregnancy, otherwise known as a tubal pregnancy. A tubal pregnancy is very dangerous and a woman should always seek prompt medical attention if one is suspected. While a laparoscopic procedure to check the full function of fallopian tubes is not possible, the tubes can be tested to check for obstruction or blockage which could lead to infertility. With a hysterosalpingogram, a doctor will use an opaque dye to make sure that fallopian tubes are open. Tubal insufflation is used to check the status of the tubes and a dye is injected into the uterus and should pass through the tubes without incident if no blockage is present.
Sexually transmitted diseases like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and pelvic inflammatory disease can affect the fallopian tubes and the ovaries, and if not treated it can lead to infertility. Ovaries in a woman secrete estrogen and progesterone, hormones which are responsible for female sexual characteristics during puberty and later in life responsible for being able to maintain a pregnancy. If the ovaries are blocked, damaged or injured, it can make a woman unable to conceive and if not treated, it can prevent pregnancy indefinitely. Ovaries and fallopian tubes play a very important role in the fertility of a female and when one or both is not present, it can lead to problems with a hormonal imbalance and infertility. A woman should always have a pelvic exam once a year to ensure the tubes and ovaries remain healthy and to avoid any problems should she decide to try and become pregnant.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...