
Definition of OCD
OCD stands for obsessive compulsive disorder. It is one of the many anxiety disorders known to modern medicine and science and it commonly involves intrusive thoughts associated with worry, fear, apprehension and uneasiness and it may also involve repetitive types of behaviors which exist simply to reduce those intrusive thoughts. Some cases of this medical condition may involve a combination of obsessions and compulsions at the same time. The most common symptoms associated with obsessive compulsive disorder include various different types of nervous rituals, aversions to particular numbers, preoccupation with religious, violent or sexual thoughts, extreme hoarding, repeated double checking of things and excessive cleaning or washing. These symptoms may cause a lot of emotional problems and they may prevent the person from functioning normally on a daily basis. Eventually, this may end up in psychotic and paranoid acts.
Statistics
Obsessive common disorder is one of the most common mental disorders. It is the fourth most common one in the United States, as there are more 2.2 million American citizens affected by OCD each year. There may even be more cases, because a large number of people tend to endure the disorder for years before finally seeking professional help. A person may have serious problems in life because of OCD because the condition may affect his or her financial independence, employment status, level of education and the overall quality of life. People from all different ethnic groups and all different age groups may be affected by it. Obsessive compulsive disorder affects men and women equally. The total costs of OCD each year add up to approximately 6 percent of costs for all mental illnesses.
Causes of OCD
Obsessive compulsive disorder is commonly triggered by a vast array of different types of biological and psychological factors. Psychological factors may be related to certain evolutionary advantage, but only in moderate cases of obsessive compulsive disorder. As far as biological factors go, scientists believe that obsessive compulsive disorder may be associated with certain abnormalities with a neurotransmitter called serotonin. Certain genetic mutations of the gene which is responsible for the transportation of the aforementioned neurotransmitter may also be associated with the development of obsessive compulsive disorder. Certain cases of obsessive compulsive disorder in children may be triggered by group A streptococcal infection.
Obsessions and Compulsions
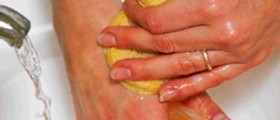
Obsessions are certain types of intrusive thoughts which tend to reoccur in a repetitive pattern and even though the person affected is fully aware that they are completely irrational, he or she cannot shake them off. Compulsions are repetitive types of behavior which occur in people who suffer from obsessive compulsive disorder as a reaction to anxiety triggered by the aforementioned obsessions. There are certain cases of obsessive compulsive disorder which do not include any overt compulsions and these cases are commonly referred to as purely obsessional OCD. People who suffer from OCD can be divided into several different categories. There are washers who are constantly obsessed by cleanliness and they are constantly afraid that they might get contaminated or that they might contaminate other people. There are also people who are referred to as checkers, as they are known for always checking things as locks, open windows, and such multiple times as they are constantly obsessed with harm or danger. There are also those who can be referred to as sinners and doubters because they constantly tend to do everything perfectly simply because they are afraid that otherwise they will be punished severely. Counters and arrangers are those who simply need to find order and symmetry in everything that surrounds them. These people are also known for constantly having various superstitions associated with specific numbers, colors and particular arrangements. The last group of people who suffer from obsessive compulsive disorder are hoarders. These people are characterized by being very afraid of throwing things away because they believe that doing so may cause certain bad things to happen to them.
Diagnosis of OCD
Obsessive compulsive disorders may be formally diagnosed by a clinical social worker, psychiatrist, psychologist or any other licensed mental health professional. A person diagnosed with obsessive compulsive disorder suffers from obsessions, compulsions or both. Fortunately enough, obsessive compulsive disorder may be treated by utilizing certain methods. The most commonly used method for the treatment of OCD is cognitive behavioral therapy. This type of therapy consists of two main types of components and in some cases it may be accompanied by certain types of prescription antidepressants. The first component of the therapy requires the patient to be repeatedly exposed to the sources of his or her obsessions and then gradually learn how to refrain from compulsions which occur as reactions to anxiety. The second component of cognitive behavioral therapy is based on the healthy and effective ways of responding to obsessive thoughts. Family therapy and group therapy are also highly recommended.


-Causes,-Symptoms,-Diagnosis-And-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)













Your thoughts on this
Loading...