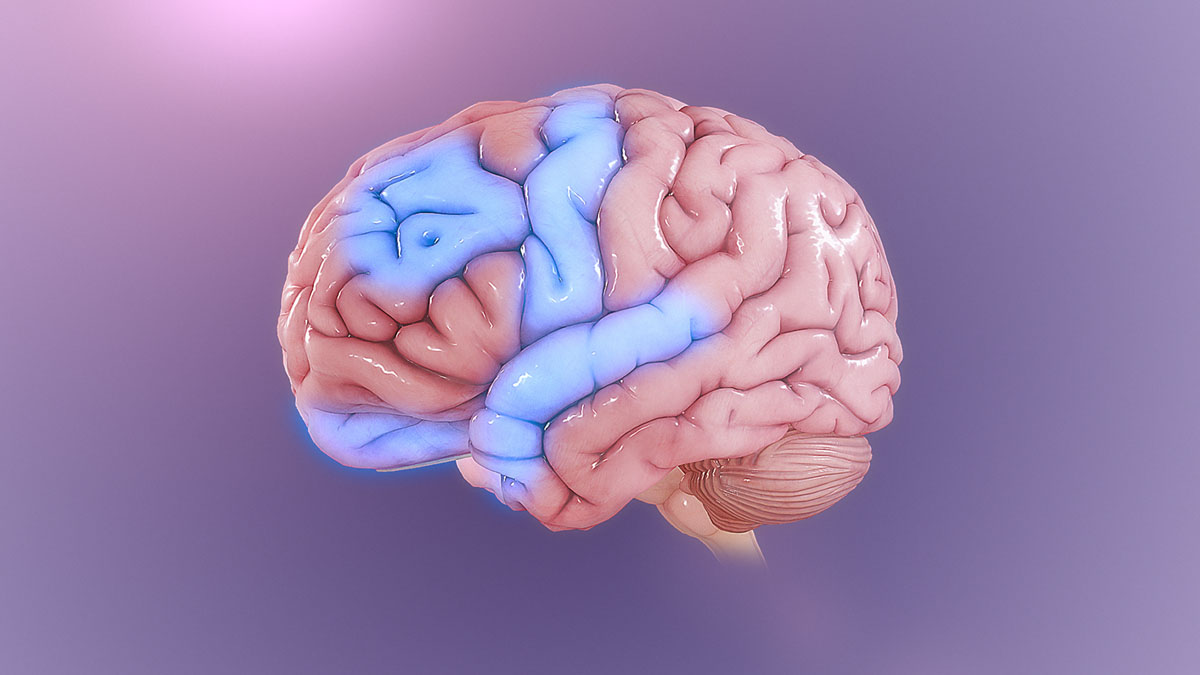
obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
Obsessive-compulsive disorder is an anxiety disorder. It is marked by inability to control unwanted thoughts, sense of obligation to follow ritual behaviours that are usually repetitive. Most people are aware of the OCD state and the irrational nature of obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviours. Depending on the intensity of the disorder people are able or not to resist these impulses. OCD sets the brain in a loop focused on certain thought or urge. These include rechecking if the light switch is turned off ridiculous number of times in a row, seeing a certain order in things and tending to it obsessively, going through equations or situations to make sure they’re done in the right order many times in a row.
obsessive-compulsive disorder therapy
Cognitive-behavioural therapy is considered to be the most efficient treatment for OCD. Although antidepressants can be used to accompany the treatment, drugs do not influence the OCD symptoms directly. Catastrophic thoughts and exaggerated sense of responsibility are the main focus of cognitive therapy. Important part of cognitive OCD therapy is learning healthy and efficient solutions for responding obsessive thoughts without resorting to compulsive behaviour.Exposure and response prevention method works by repeatedly exposing the OCD individual to the source of their obsession and asking them to refrain from the anxious urge to act compulsively.By doing this they learn to realise that their anxiety can go away on its own, without performing their ritual. This way the control over obsessive thoughts and compulsive reaction gets gradually re-established.
Four Steps of Conquering Obsessive Thoughts and Compulsive Urges The four steps of conquering OCD are relabel, reattribute, refocus and revalue.Relabel means recognizing the relation of obsessive thoughts and urges and OCD. Repeatedly facing and explaining oneself this relation is the first step to regaining control over the OCD state.Reattribute is realization that the intrusiveness and intensity of thought or urge that causes the anxiety are results of OCD. OCD can be a result of biochemical imbalance in the brain. This way the OCD individual gains realization that brain can generate false messages that have no relevant meaning and can be ignored.
Refocus concentrates on working around OCD thoughts by diverting attention to something else for couple of minutes, and concentrate on performing a different behaviour and resisting the urge to act compulsively.Revalue is learning that OCD thoughts are not relevant. Even though they are present, they are not significant. Therefore they have no power to cause discomfort and anxiety.




-Causes,-Symptoms,-Diagnosis-And-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)











Your thoughts on this
Loading...