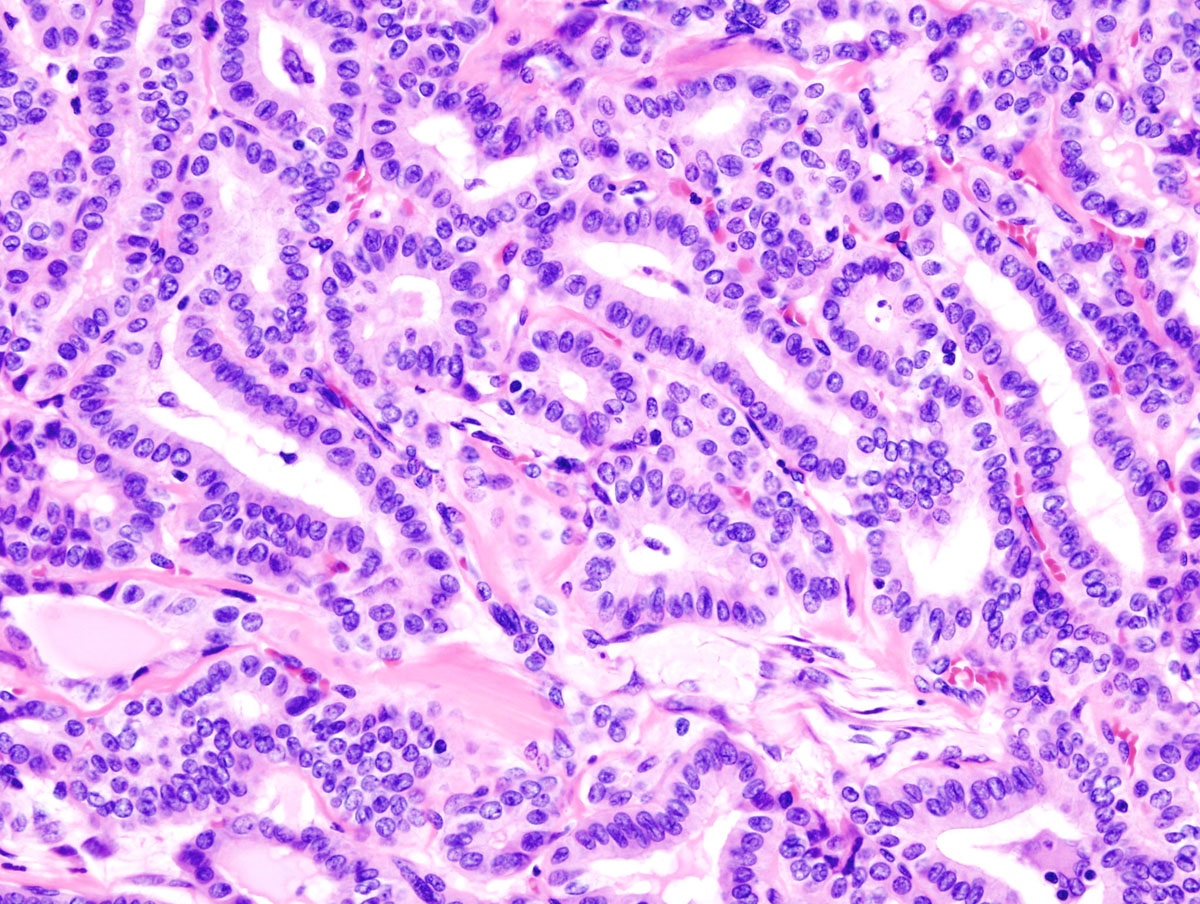
Thyroid Gland OverviewThe thyroid is a crucial endocrine gland in the body as it has an influence on every cell. It is located in the neck, below the Adam’s apple. The thyroid gland excretes hormones that control different metabolic processes. Thyroid hormones are thyroxine (T4) and triiodothhyronine (T3) that regulate growth, energy use and protein production. In order to produce these hormones, the thyroid gland requires iodine, tyrosine and selenium, which can be obtained from foods. Deficiency of these nutrients can cause thyroid problems. Common disorders of the thyroid gland are hypothyroidism or underactive thyroid gland and hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid gland.
Hypothyroidism and HyperthyroidismUnderactive thyroid gland or hypothyroidism occurs when the gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). Hypothyroidism results in sluggish metabolism and other associated symptoms that develop slowly, over years. Common symptoms of underactive thyroid gland are: increased sensitivity to cold, constipation, unusual weight gain, hair loss and pale, dry skin. Reduced heart rate, increased cholesterol level, hoarse voice, joint pain and muscle weakness are also present. Hypothyroidism is additionally followed with lethargy, depression and slowed thinking.
However, the symptoms may range from mild to severe. Myxedema coma is the most severe form of hypothyroidism. It is actually a life-threatening complication of this thyroid disorder marked by the loss of brain function, which occurs due to severe and long hypothyroidism.
On the other hand, hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid gland is a condition characterized by unexplained weight loss, nervousness, anxiety, tremor and abnormal heart beat. This disease results out of overproduction of T3 and T4 hormones. This is usually due to an autoimmune disease known as Grave’s disease. In hyperthyroidism, metabolism is dramatically accelerated. Other symptoms of hyperthyroidism include: excessive sweating, increased appetite, heat intolerance and difficulty sleeping.
Diagnosis of Thyroid DisordersHyperthyroidism can be identified with the help of a blood test and a physical exam. Hypothyroidism is diagnosed by measuring THS level in the blood. TSH is a thyroid-stimulating hormone that is produced by the pituitary gland and that controls the thyroid.
Treatment for Thyroid DisordersConventional medical treatment for hypothyroidism involves replacement of the deficient thyroid hormone with Levothyroxine. On the other hand, alternative treatments for underactive thyroid include the use of herbal supplements. One of the most effective natural treatments for hypothyroidism are Hypothyrex, which includes organic herbal extracts, vitamins and minerals. Use of this therapy can effectively replace a hormone therapy for thyroid disorders. Unlike with conventional treatment options, this natural treatment does not have to be taken life-long.








-In-Adults_f_280x120.jpg)

Your thoughts on this
Loading...