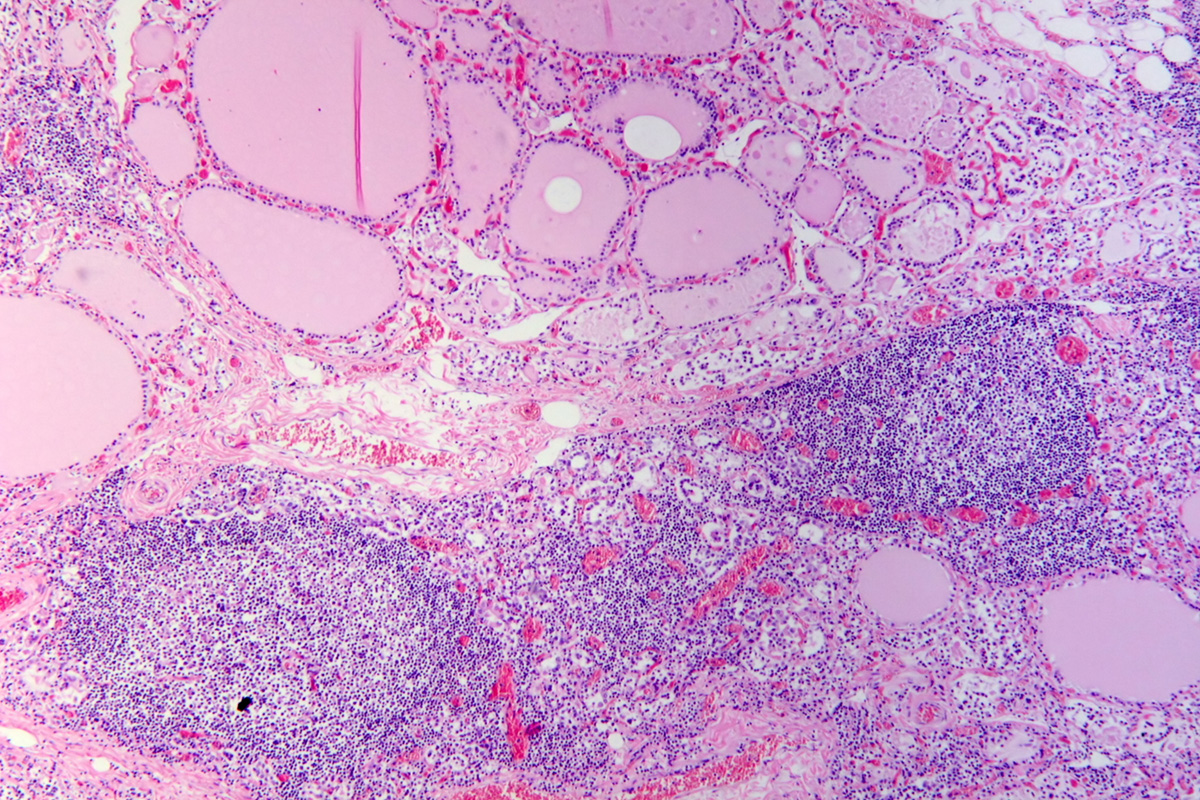
The thyroid gland, which is located in the neck, produces two hormones (T3 and T4) essential for body metabolism. In order to produce sufficient amount of hormones thyroid gland is stimulated by TSH, the hormone produced by the pituitary gland. T3 and T4 thyroid hormones require optimal amount of iodine which is obtained from certain foods. Once the thyroid gland has finished synthesizing its hormones, they are released into the blood and start regulating many metabolic processes.
Thyroid disorders represent a group of illnesses that feature with improper production of thyroid hormones. In some cases the production of these hormones is increased (hyperthyroidism) and in other the production is decreased (hypothyroidism). Both of these cases feature with distinguished symptoms and signs and if not diagnosed and treated on time may cause serious complications.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
In case there is an excess of thyroid hormones a person is suffering from hyperthyroidism. This condition typically leads to excessive sweating, rapid weight loss (in spite of increased appetite and intake of food), sensitivity to heat, high blood pressure, rapid/ irregular heart beat, tremor of the hands, problems with sleeping, anxiety and irritability.
Increased production of the thyroid hormones can be induced by many illnesses of both, the thyroid gland and the pituitary gland such as thyroid nodules, Grave's disease, thyroiditis, pituitary adenoma etc.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a thyroid disorder in which the gland does not produce sufficient amount of thyroid hormones. The most common symptoms of hypothyroidism are dry skin, excessive sleeping, sensitivity to cold, low blood pressure, sluggishness, muscle weakness, constipation and weight gain.
Hypothyroidism is in majority of cases caused by Hashimoto thyroiditis (an autoimmune disorder). It also occurs after surgical removal of the thyroid gland (partial or total) as well as after administration of radioactive iodine in case of thyroid gland cancer.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Thyroid Gland Disorders
The level of T3, and T4 as well as TSH is essential for evaluation of the function of the thyroid gland. Elevation or decrease in the level of certain hormones points to hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
Treatment of thyroid disorders depends on whether a patient is suffering from hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. In case of hypothyroidism patients require lifetime substitution with thyroid hormones. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism may be treated with anti-thyroid drugs, beta blockers and in case of tumors or toxic adenomas patients undergo surgery. Some patients suffering from hyperthyroidism are also treated with radioactive iodine treatment. Hyperthyroidism can with certain treatments be reversed into hypothyroidism and these patients eventually need hormonal substitution therapy which provides with optimal level of thyroid hormones.








Your thoughts on this
Loading...