Myelogram as a Medical Procedure
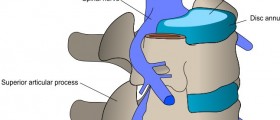
Myelography is another term used for this type of diagnostic test, which is usually suggested by doctors in cases when spinal cord, meninges and nerve roots have to be examined, to see if any abnormalities are present. The procedure is done with the help of X-rays and a contrast material that needs to be administered in the subarachnoid space.
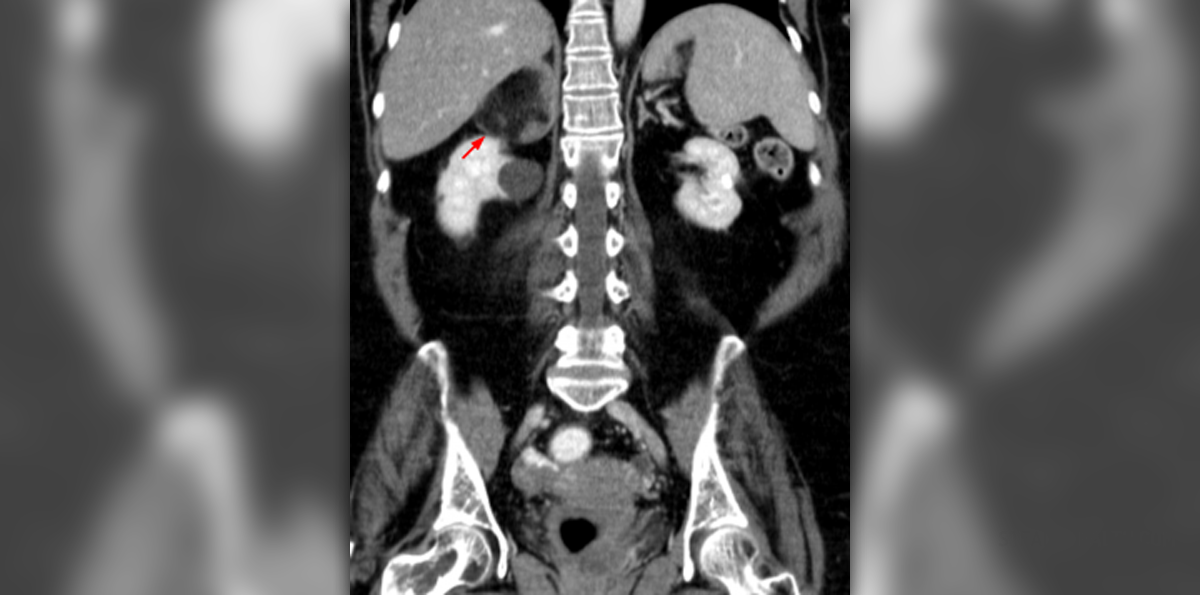
Unlike the results of an ordinary X-ray, which show only the bones, the results of myelography provide a detailed image of the spinal cord, the nerves and the canal, which allows the doctors to make a diagnosis. With the help of this test, conditions such as disc herniation, bone spurs and spinal stenosis can be detected as well as tumors and infections. This procedure is done very quickly, it takes about an hour and the patient can go home the same day./
It is necessary to stay in the hospital for a few hours for observation, but after that, if everything is all right, the patient can go home. There are some rules that have to be followed after the procedure, at least for the first 24 hours, to avoid possible complications or side effects.
Risk and Side Effects Associated with Myelogram
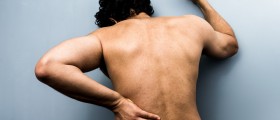
The fact is that risk and side effects are minimal with this procedure, and they occur in approximately 5 to 10 % of the patients. They consist of mild headaches, and negative reaction to the contrast material, which is usually manifested through nausea, itching, or even sneezing.
It is also possible that bleeding around the nerve roots or an injury to the nerve can occur when the needle is inserted into the spinal canal, but these complications are very rare. Pregnant women should not undergo myelogram, and the doctor should be informed about the presence of diabetes, asthma, or problems with kidneys, heart or the thyroid gland, if any of them exist.
Also, people who suffer from some allergy should notify the doctor about it, because such information help in reducing the risks. Since excessive exposure to radiation makes people more at risk of developing some type of cancer, this applies for myelogram as well.
Myelogram Study
- Forty-three patients had headache on the day of examination and 22 the next day. Twelve noted dizziness. Seventeen were nauseated and 11 vomited on the day of examination.
- Thirty-one of the patients complained of muscular pain in various parts of the body. The pain was different from that of the presenting complaints. The lower back and legs were the usual locations, but neck pain was also frequently reported. We interpreted this pain as caused by spinoradicular irritation.
- Two patients noticed a high-frequency tone, and one patient heard bell-ringing for several hours.
- The symptoms varied considerably. Hemianopia occurred in one woman and lasted for several hours. Previously in this patient, this symptom had occurred only in association with headache. Three patients noticed cloudiness of vision, four saw spots and stripes, and one experienced changes in color vision.
- One patient had, in addition to confusion, amnesia, and hallucinations, moderate dysphasia and dysarthria. Three other patients had mild dysarthria during the first 24 hours after myelography.
- There were two patients with pronounced neuropsychologic symptoms. After thoracic myelography, a 60-year-old man experienced considerable confusion in addition to almost complete memory loss for recent and more distant events. He experienced visual and auditory hallucinations as well as dysarthria and dysphasia lasting 24 hours. He recovered completely over the next 24 hours.
- Four patients had visual hallucinations, another had auditory hallucinations only, and another had both visual and auditory hallucinations. The hallucinations lasted between a few minutes and 4 - 5 hours.
- Twelve patients experienced changes in mood the day of the examination. Seven patients had a vague feeling of unease and anxiety, and two of them also felt depressed and cried more easily than usual. One patient had an anxiety reaction. Six felt depressed and were unusually worried about their illness and what it would mean for them in the future.
- Twenty-six patients complained of a restless night after metrizamide myelography. This varied from frequent awakenings to unpleasant nightmares. Several of the patients described being half-asleep with intermittent dreaming.



-Causes,-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)





Your thoughts on this
Loading...