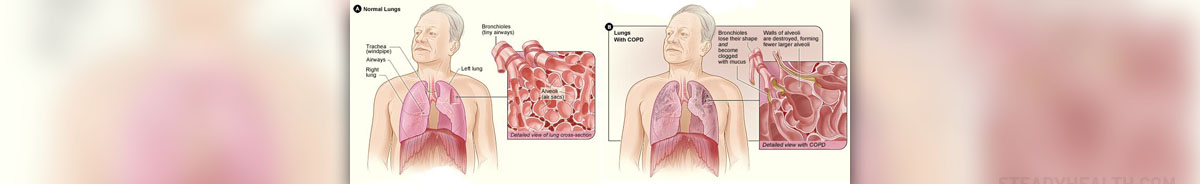
What exactly is COPD?
COPD is an acronym that stands for the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Since, it actually refers to the group of lung diseases that have the damage of airways as a common symptom, the two main diseases are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It is not at all rare that people suffering from COPD may have both of them. The reason why several diseases comprise this group is related to the fact that the majority of them is caused by smoking, which means that the same majority may be prevented if the person quits smoking very soon, or if not smoking at all. Besides cigarette smoke, irritants such as secondhand smoke, pipe smoke, and air pollution may cause chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which means that those who are exposed to these irritants are at higher risk even if they themselves do not smoke.
How can it be treated?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease causes permanent damage to the lungs, and this damage cannot be reversed, which means that there is no way for lungs to be healthy ever again, but the treatment of the symptoms which are the consequence of such damage is possible to a certain extent, and it is possible to decrease the risk of some complications. The doctor will suggest the most appropriate method or even the combination, after gathering all the necessary information regarding each particular case.
First of all, the most important thing for a person who smokes is to quit this nasty habit, because that is the only way to prevent worsening of the condition. It is not easy, but when having in mind the complications that are practically inevitable if the person continues to smoke, it should not be hard to choose the priorities. Second of all, there are medications such as bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and antibiotics that simply have to be used. Bronchodilators relieve the coughing and make breathing easier by relaxing the muscles around the airway, while inhaled corticosteroids work by reducing the inflammation of the airway thus also making the breathing easier. Antibiotics are used in the treatment of respiratory infections. The third option is related to the surgery, but this is suggested only in extremely severe cases in which medications aren’t helpful. Either lung transplantation or lung volume reduction can be performed, but both of the procedures carry a significant amount of risk. Moderate, but even some severe cases, can be treated with the so-called oxygen therapy, because it can also improve the function of the heart and the quality of life in general.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...