Tobacco smoking is an old practice that began as early as 5000 to 3000 BC. Tobacco was introduced in Eurasia in the late 16 century and since then it was met with severe criticism. However, tobacco smoking managed to become very popular despite the fact it is associated with the most deadly diseases, since 1950. As of 2000, more than 1.22 billion people are practicing smoking. The rates of consumption continue to grow in the developing world, and the gender gap declines with younger age. Men typically smoke more than women, but the difference is becoming more and more irrelevant. Smoking is a direct cause of many heart and lung diseases, including heart attacks, strokes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema and cancer. Here is a quick review of some of the most severe lung diseases caused by smoking.
Chronic bronchitis
This condition is characterized by the chronic inflammation of the bronchi in the lungs. Bronchi are medium sized airways in the respiratory tract that conduct air into the lungs. In chronic bronchitis, these airways are constantly inflamed and narrowed, which makes breathing very difficult. Patients typically complain about shortness of the breath, wheezing, chest pain, cough and green or yellowish sputum. Moreover, their whole body is deprived of precious oxygen, since the breathing process is severely disturbed and the lungs are not being filled by air properly.
Emphysema
This is a long-term progressive disease of the lungs that is primarily characterized by the shortness of breath. This symptom occurs since the tissues that support the physical shape and function of the lungs are destroyed. Destruction of the lung tissue around the alveoli makes these sacks unable to hold their shape upon exhalation, which makes the airflow impaired and traps the air. As a consequence, people with emphysema do not get enough oxygen, but they also fail to remove carbon dioxide from their system.
Lung cancer
This is the most severe consequence of prolonged tobacco smoking. Lung cancer is defined as a disease in which the cells in the tissues of the lung start growing out of control. Sometimes, the growth may lead to metastasis and invade tissues beyond the lungs. Lung cancer is responsible for 1.3 million deaths worldwide each year. It usually begins with classic symptoms of lung irritation such as shortness of breath or coughing. However, sometimes the patients may cough up blood and experience dramatic weight loss. Only 15% of people with lung cancer are nonsmokers and their disease is normally result of a combination of genetic factors or exposure to radon gas, asbestos and air pollution.
- www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/fact_sheets/health_effects/effects_cig_smoking/index.htm
- www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/sgr/50th-anniversary/pdfs/fs_smoking_respiratory_508.pdf
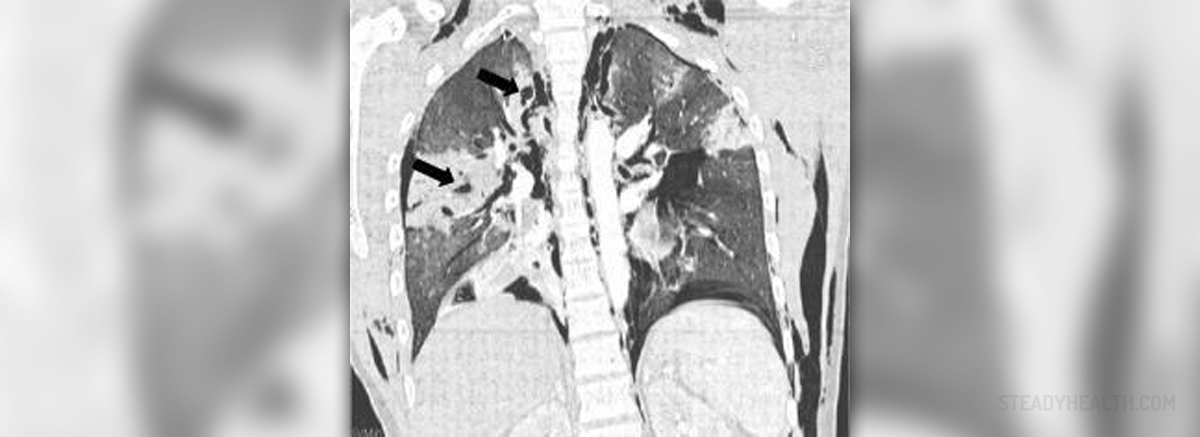
- Photo courtesy of Morgan Le Guen, Catherine Beigelman, Belaid Bouhemad, Yang Wenju00efe, Frederic Marmion by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Lung_lacerations.JPG














Your thoughts on this
Loading...