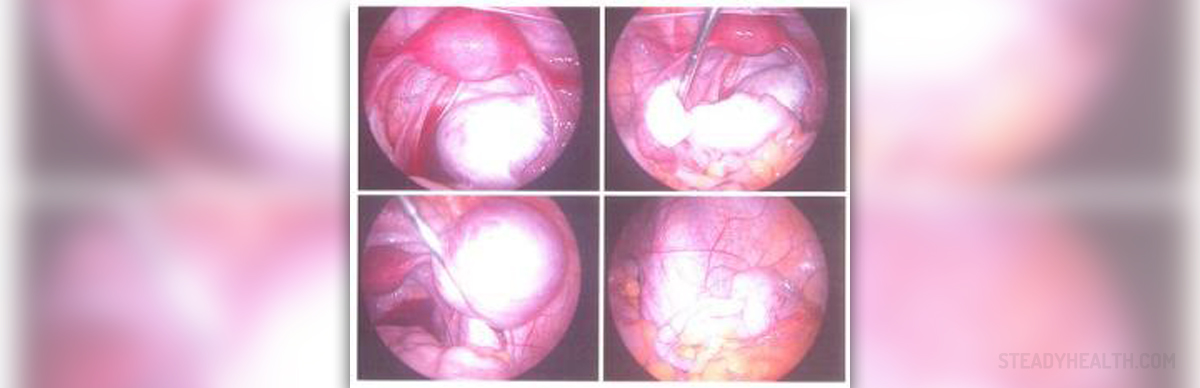
Endometriosis is a state in which tissue similar to the lining of the uterus is placed elsewhere in the body. The growth usually develops in the pelvic area, outside of the uterus, on the ovaries, bowel, rectum, bladder, and the frail lining of the pelvis.The main sign of a possible endometriosis is pain, although many women affected with this disease do not have any symptoms.It is a progressive disease, which may result in infertility, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia and low back pain. To make a diagnosis, the doctor has to evaluate the patient’s symptoms, check medical and gynecological history and family history of endometriosis. After this, the doctor should carry out a short physical examination and a detailed pelvic examination. A final diagnosis can be made only by pelvic laparoscopy.
Prevention and Treatment
There is no way to prevent endometriosis. Nevertheless, the condition may stop developing briefly if the patient uses oral contraceptives or becomes pregnant. There are several different treatment options and some include medications to control pain (such as ibuprofen or naproxen), pain management combined with control of hormone levels (drugs that can have this advantage involve oral contraceptives, progesterone, danazol and medicines known as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, such as nafarelin and leuprolide), hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) and conservative surgical treatments (laparoscopy and laparatomy).
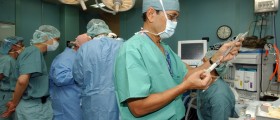
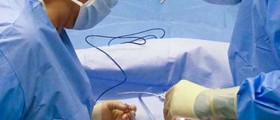
Laparoscopy is a procedure during which the surgeon inserts the laparoscope into the abdomen through a small cut. This surgical procedure may be used to diagnose and treat endometriosis. The procedure is done under the anesthesia. During this surgery, three or four cuts may be made in the woman’s lower abdomen. Endometrial growths may be removed with a surgical knife or destroyed by laser or electric current. Tissue parts can be taken for biopsy through the laparoscope.After the surgery, the patient is moved into the recovery room where she usually spends a couple of hours. In some cases, the patient needs to stay in the hospital over the night. However, the patient will probably be able to return to her normal activities after a week. For the first two or three days after the laparoscopy, women are tired and weak. In the time of recovery period, the patient will probably need some help. The patient also may feel numbness at the cut site.
Other risks which are connected with this surgical procedure involve possible complications because of infection (antibiotics are usually given to prevent this), anesthesia, injury to organs or other structures, and bleeding into the abdominal hole.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...