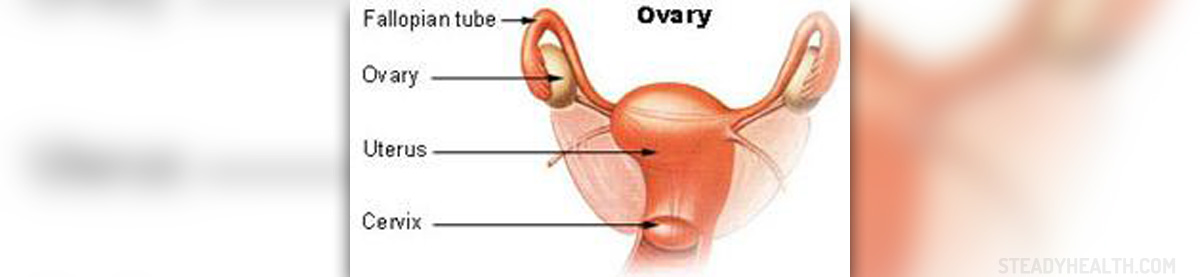
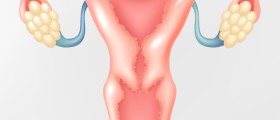
Different growths and cysts in the ovaries are in some cases resolved using surgical procedures. These can be ovarian cysts, fibroids, various adhesions or some pelvic infection and all of them should be taken care of. Surgeries may involve removal of noncancerous cysts, which is procedure known as cystectomy, or removal of one or both ovaries if there is some cancer.
Reasons for surgery
There are several reasons for performing any surgery on the ovaries. This includes: masses (growths) in both ovaries and cysts larger than 3 inches (or 7.6cm) in diameter. Cysts which don’t resolve or get smaller after several months of monitoring, as well as some non-functional cysts seen on the ultrasound should also be surgically treated. Postmenopausal women, women who use birth control pills and those who never had a menstrual period and have been diagnosed with ovarian growths should also be considered for ovarian surgery. Suspicion for ovarian cancer or use may also be the reason to have this surgical procedure.
Surgery for Ovarian Problems
In most cases doctors advise their patients to have laparoscopy surgeries, when the surgeon makes small incisions and performs the whole procedure through them, using special equipment. Another possible option is laparatomy procedure, which requires somewhat larger incision on the abdomen. Laparatomy is frequently used in patients when there is some suspicion to any type of cancer, because this procedure enables the surgeon to have the best possible view of the abdominal and female pelvic organs. Also, surgeons may remove ovarian cancer during this procedure if they happen to came across to it.
Postoperative
The surgery is normally performed under general anesthesia. After the laparoscopy surgery, patients may be back to their normal everyday routine after 24 hours, but doctors advise avoiding physical exercise or some strenuous activities for another week or so. Laparatomy for ovarian cysts usually requires hospitalization and 2 to 4 days of recovery in the hospital and further 4 to 6 weeks of recover at home. Possible Risks of Ovarian Surgeries
Even after the patient has undergone surgical removal of the cyst on the ovaries – cyst may come back again. On the surgical site, some patients may form adhesions (scar tissue). The same problem may appear in the pelvis, on the fallopian tubes or on the ovaries. Women may develop certain infections as the result of this surgery or pain after the surgical procedure may become un-controlled. In rare cases, patients may experience some damage of the bladder or the bowels.
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/ovarian-cyst/treatment/
- www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/ovarian-cysts
- Photo courtesy of Magnus Manske by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ovary_nih.jpg











Your thoughts on this
Loading...