A type of Arthritis
There are many different types of arthritis affecting humans. Juvenile ankylosing spondylitis (JAS) is only one of them. This medical condition affects only the spine and is reported to occur in people between 17 and 35 years of age (hence the term juvenile). Still, it may affect younger and older individuals too. The term ankylosing refers to stiffness or rigidity, a typical characteristic of the disease. According to the available data, JAS is more frequent among men. As a matter of fact males develop JAS 2-3 times more compared to females.
The very disease is characterized by inflammation of large joints of the spinal column. The affected joints are painful and stiff which significantly interferes with very day activities. Inflammatory process is the one blamed for erosion of the joint between the spine and the sacroiliac bone, bone bridges that form between nearby vertebrae and subsequent bone fusion and finally, fusion of the chest bones.
JAS is together with psoriatic arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and Reiter's syndrome a member of so called spondyloarthropaties. All of the mentioned conditions are responsible for inflammation of the spine/sacroiliac joints, they run in families and none of the affected patients has increased level of rheumatoid factor (RF), an antibody that is detected in blood of patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis and other rheumatoid diseases.
When it comes to underlying causes of JAS, the condition is considered multifactorial. This means that many different factors trigger the onset of the disease. Genetic factors are commonly combined with environmental. Scientists have confirmed that HLA B27 antigen plays a significant role in whether the child will or will not end up with JAS. The presence of this antigen makes the child susceptible to condition but this does not actually mean that JAS will develop for sure.
What are Symptoms of JAS?
Symptoms and signs of JAS are intermittent meaning they occur from time to time. The course of the disease and its characteristics are not unique and each and every child practically has different clinical presentation of the disease.
In the majority of cases, however, patients experience back pain (more severe at night and during rest), muscle rigidity in the morning, stooped posture associated with intense back pain and inability to take deep breaths (if there is fusion of the joints between the ribs and spine). Additionally, one may suffer from loss of appetite and weight loss, fatigue, fever and anemia. Still, the major problems these patients have to deal with are joint pain and pain at the site of attachment of muscles/tendons and ligaments to bones. Finally, some patients develop painful eye inflammation and it is also possible to have other organs affected (the heart and lungs).
Management of JAS
Initially all patients undergo a thorough physical exam and doctors take patient's medical and family history. Additional tests are simply inevitable for the diagnosis to be confirmed. So treatment may only begin once the final diagnosis is established.
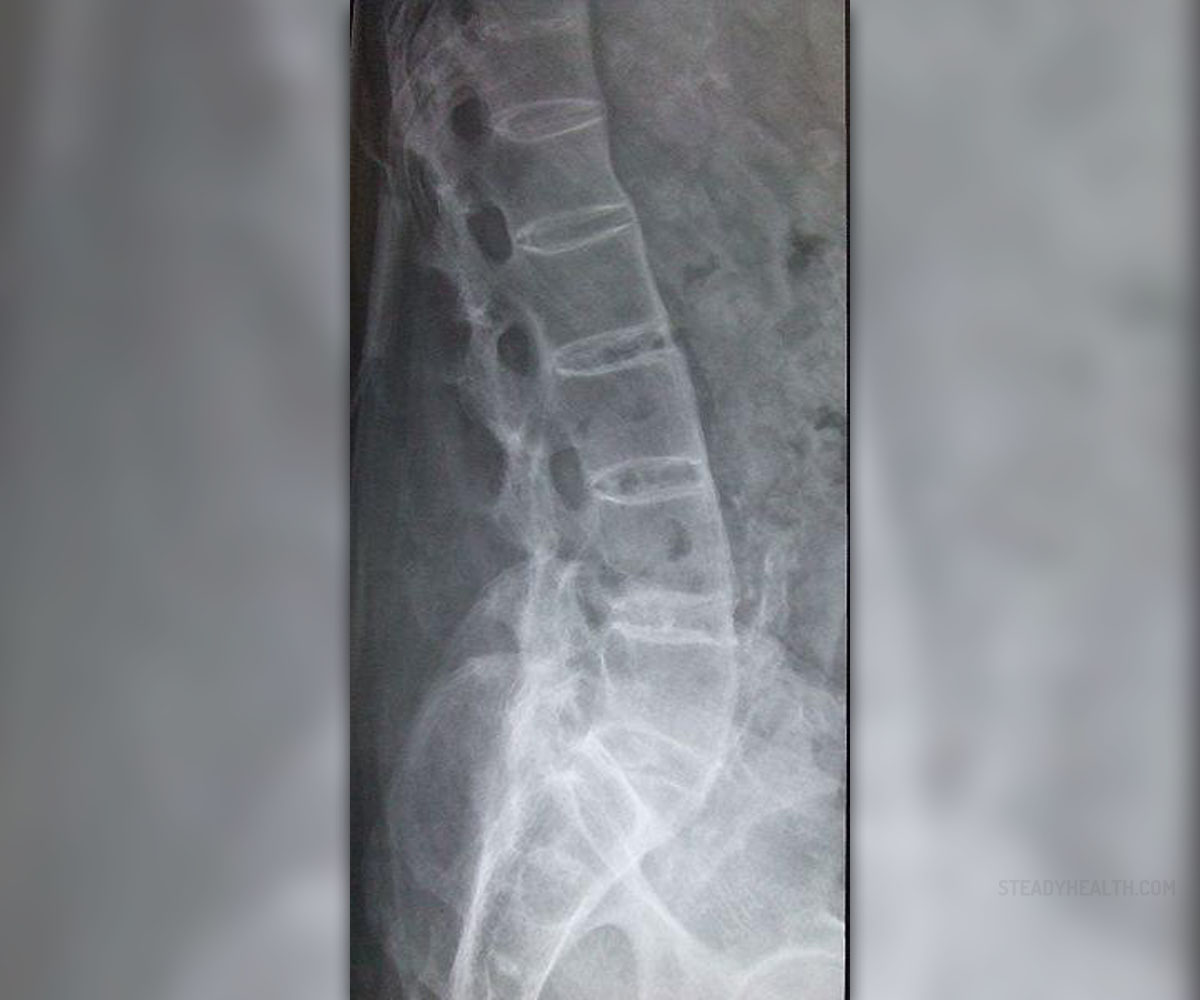
First of all, doctors perform blood tests. They look into blood cell count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), markers for inflammation and they also check the presence of antigen HLA B27. This antigen is identified in most patients suffering from JAS although it does not have to be detected in some cases. X ray is a diagnostic test that provides insight in the structures of the spinal column. It may reveal damage to different joints, bone fusion and other skeletal changes associated with JAS. Doctors may also recommend aspiration of the affected joints and microscopic evaluation of obtained samples.
Even though there is actually no cure for JAS, there are many treatments available that can significantly help patients. Doctors create an individual treatment plan according to clinical and laboratory findings. The goal is to bring symptoms under control. This particularly refers to pain and stiffness. Additionally, it is important to prevent potential complications such as skeletal deformities and allow patients to live normal and active lives.
Treatment may be solely medicamentous comprising various drugs. For example, some patients respond well to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) and they require no additional drugs or other treatment options. Furthermore, inflammation may be more severe. In this case doctors opt for a short course of corticosteroids. Maintaining proper posture is achieved with regular exercise. Each and every exercise program pays attention to exercises that strengthen back muscles. Physical therapy is also vital and an integral part of the overall JAS treatment.
As for progression of the disease, scientist have estimated that diagnosis is generally established 15 years after the onset of initial symptoms. It is also possible to first experience symptoms related to joints outside the trunk and only later develop typical changes in the spinal column.
All in all, prognosis is not so good if the disease starts early in childhood and may cause severe health problems after certain number of years in spite of aggressive treatment.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...