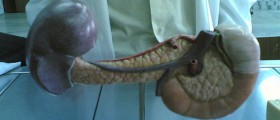
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of pancreas, a very important gland that is located in the abdomen. The primary function of this gland is production of digestive enzymes as well as production of certain hormones among which insulin is the most important.
Pancreatitis develops as a consequence of autodigestion of the gland. This occurs in cases of chronic alcohol abuse, in case of obstruction of excretory canals of pancreas (tumors, gallstones) etc. Certain medications and viral infections can lead to pancreatitis as well. Pancreatitis can be acute and chronic.
The symptoms of acute pancreatitis develop suddenly while chronic form of the disease leads to gradual deterioration of the glands structure and function. In acute form of the disease the attack is sudden and followed by sudden pain in abdomen. The pain intensifies and can last for a few days. It is located in the middle of the abdomen with tendency to irradiate towards back. Nausea and vomiting as well as loss of appetite are regular symptoms. The abdomen is sensitive to touch. Depending on the cause of pancreatitis one may develop jaundice. Complications such as pleurisy may occur. In case of severe hemorrhage in pancreas lethal outcome is inevitable. Chronic form of the disease features with prolonged abdominal pain and changes in stool (diarrhea, oily stool etc.). Chronic pancreatitis leads to serious undernourishment.
The diagnosis can be set after examination, blood tests that present increased levels of pancreatic enzymes such as amylase and lipase. Ultrasonography of abdomen shows the signs of inflammation. Even CT scan can be helpful. In chronic pancreatitis patient's stool is rich in fats as these cannot be absorbed properly.
The treatment has to start as soon as possible to prevent further damage of the gland and reduce the intensity of symptoms. Unfortunately the parts of the gland that have been demolished cannot be replaced as this organ does not posses regenerating abilities.
In mild cases only supportive therapy is administered. Hospitalization is done in all cases. Patient is held in hospital for up to 16 days. A patient is not allowed to eat because the food will induce further production of enzymes hence lead to additional damage. Instead of that intravenous fluids are given. Stomach acid is removed by usage of tubes that are placed through nose into the stomach. Doctors are careful in administration of medications for pain and anxiety as some of these can be more damaging than helpful.
The surgery is left for possible complications and causes such as gallstones severe tissue damage or hemorrhage. After being discharged patient has to continue with low fat diet. This diet has to include plenty of proteins. Together with diet a patient is prescribed medications that will reduce hyperacidity.
In chronic form of the disease one is treated with medications and appropriate diet so that malnutrition and chronic pain can be overhauled. Undernourishment is delta with by intake of specific enzyme preparations. These supplements are taken regularly and help in digestion. As diabetes may be a consequence of chronic pancreatitis one may be even prescribed medications to normalize sugar levels in blood. Alcohol, smoking and food that raises the level of acidity are strictly forbidden.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...