The pancreas is a gland of major importance for the body. It is located in the abdominal cavity and it is able to produce many enzymes and hormones. There are several illnesses which affect the pancreas and significantly interfere in its function. They include acute and chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, diabetes, islet cell tumor and pancreatic cancer.
Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis
In acute pancreatitis there is a sudden and unexpected inflammation of the pancreas and sudden disturbance of its functions while chronic form of the disease leads to gradual damage to the pancreas and loss of its functions.
With acute pancreatitis, you experience severe gastric pain in the upper stomach which radiates to the back, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and loss of appetite. Furthermore, a patient may develop fever and chills and in severe cases there is a chance of hemodynamic instability with subsequent shock.
Chronic pancreatitis patients commonly complain about persistent abdominal pain. They suffer from steatorrhea (the presence of fat in the stool) since the pancreas cannot produce enzymes necessary for digestion of fats. Malabsorption eventually results in weight loss. And finally, these patients suffer from diabetes as well.
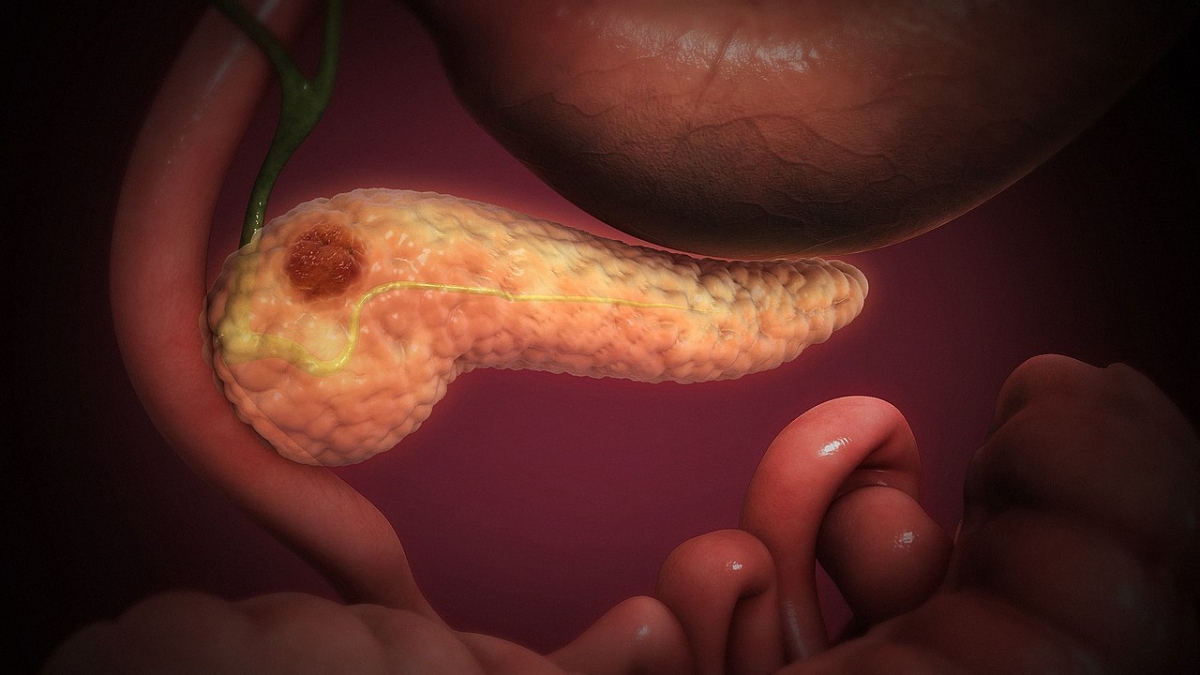
Pancreatic Tumors
Pancreatic cancer is a malignant tumor and its symptoms generally depend on the stage of the disease. The most common symptoms and signs of pancreatic cancer are loss of appetite and subsequent weight loss, stomach ache and back ache, jaundice and frequent fevers. The cancer is very aggressive and the prognosis is not encouraging.
Islet cell tumors of the pancreas are rare tumors. They can be classified according to substances they produce into insulinoma (the tumor produces excessive amounts of insulin), gastrinoma (the tumor produces excessive amounts of gastrin), glucagonoma (the tumor produces excessive amounts of glucagon), VIPoma (the tumor produces huge amounts of VIP) and finally, Somatostatinoma (the tumor produces excessive amounts of Somatostatin). The very excess of these substances leads to various symptoms and sings depending on the particular tumor type. Apart from islet cell tumors which produce different substances some of them are non-functioning meaning that the tumor does not produce any substance at all. Non-functional islet cell tumors lead to non-specific symptoms and their presence is confirmed with ultrasound, CT scan or MRI of the abdomen.
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis affects the lungs, sweat glands and the pancreas. The symptoms of the illness are associated with abnormalities with the function of the pancreas. Characteristic symptoms of cystic fibrosis include repeated respiratory infections, bronchitis and sinusitis, chronic cough, wheezing and changes in color and amount of sputum. Gastrointestinal presentation of cystic fibrosis includes pale or clay colored stools which float and are foul smelling, weight loss, failure of newborns t pass stool, abdominal pain and flatulence.
Diabetes
In diabetes type 1 the structure of the pancreas is changed. Namely, beta cells in charge with production of insulin are destroyed and the production of this precious substance is significantly reduced if not eliminated. The most common symptoms and signs of diabetes type 1 are excessive thirst and appetite, dry mouth, increased urination, unusual weight loss or gain, fatigue, nausea and vomiting and blurred vision. In women diabetes may cause frequent vaginal yeast infections. In patients suffering from diabetes wounds, sores and cuts are slow-healing.
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/pancreatic-cancer/
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/acute-pancreatitis/
- Photo courtesy of Scientific Animations Inc. by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pancreatic_Cancer.jpg











Your thoughts on this
Loading...