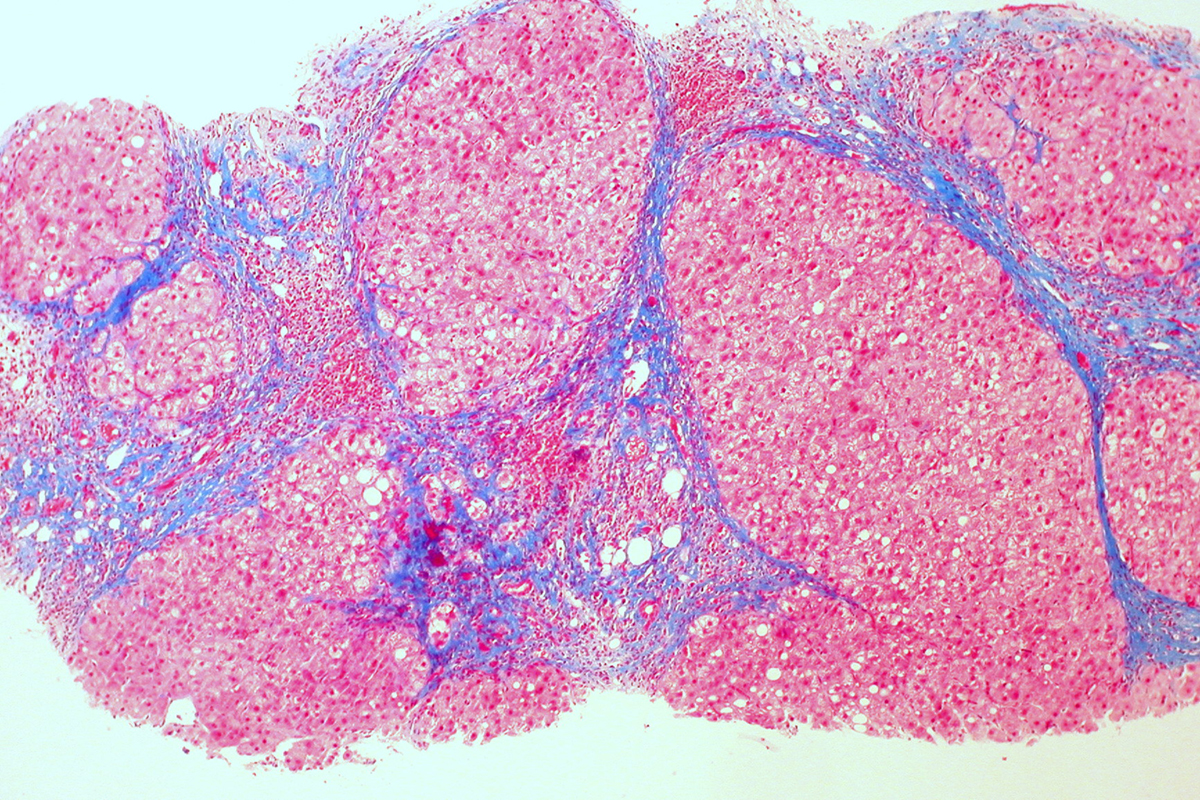
Cirrhosis is a chronic disease that affects the liver. Damage to the liver tissue prevents it form working normally and if it is not treated on time, it can lead to liver failure.
Chronic alcoholism and chronic hepatitis are two major causes of cirrhosis. Other causes include inflammation, infection, poison and heart disease.
Alcohol can lead to the death of liver cells. The body then forms scar tissue around the veins of the liver. This scarring process occurs in 10 to 20 percent of alcoholics and it is the most common form of cirrhosis in the US.
Hepatitis is the inflammation of the liver, most commonly caused by a virus. If untreated, it leads to cell death and scarring of the liver. Hepatitis B, C and D all cause cirrhosis but in the United States, hepatitis B is the most common cause.
Biliary cirrhosis is caused due to blockage of the ducts that carry bile from the liver through the gallbladder and to the intestines. If those ducts are blocked, bile returns and causes liver damage. There is also autoimmune cirrhosis, in which the immune system starts fighting liver cells and causing damage to the liver.
One of the characteristic of cirrhosis is that its symptoms are not necessarily present in the early stages of the disease. This is why some people don’t even know they have cirrhosis until there is a complication.
Symptoms are caused either by a gradual failure of liver functions or by the distortion of its shape, due to scarring. Most common symptoms include weakness and fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite and sex drive. Jaundice is one cirrhosis symptom and it results in a yellowing of the skin and eyes. Other symptoms include fever, itching, swelling in the abdomen, ankles and legs, bleeding from the gums or nose, blood in the stool or vomit and sensitivity to drugs.
In some men cirrhosis may cause abnormal breast growth or small testes in men, while in women it can cause abnormal menstrual periods.
Treatment of cirrhosis cannot reverse liver damage but it can slow down its degeneration and prevent further complications. It is essential to stop drinking alcohol and eating food rich in fats, sodium and sugars.
Some medications can be harmful for the liver, like Tylenol or ibuprofen, and their use should be discussed with a doctor. Most medical treatment is targeted to relieve the symptoms and complications of cirrhosis, but a medication that will cure it completely is yet to be discovered.
There are, however, some experimental procedures and treatments that are currently being studied. As for surgery, the only procedure that has been proven effective with cirrhosis is liver transplantation. It is an operation in which a damaged liver is replaced by a healthy liver from a donor. The survival rate in this procedure is 80 to 90 percent.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...