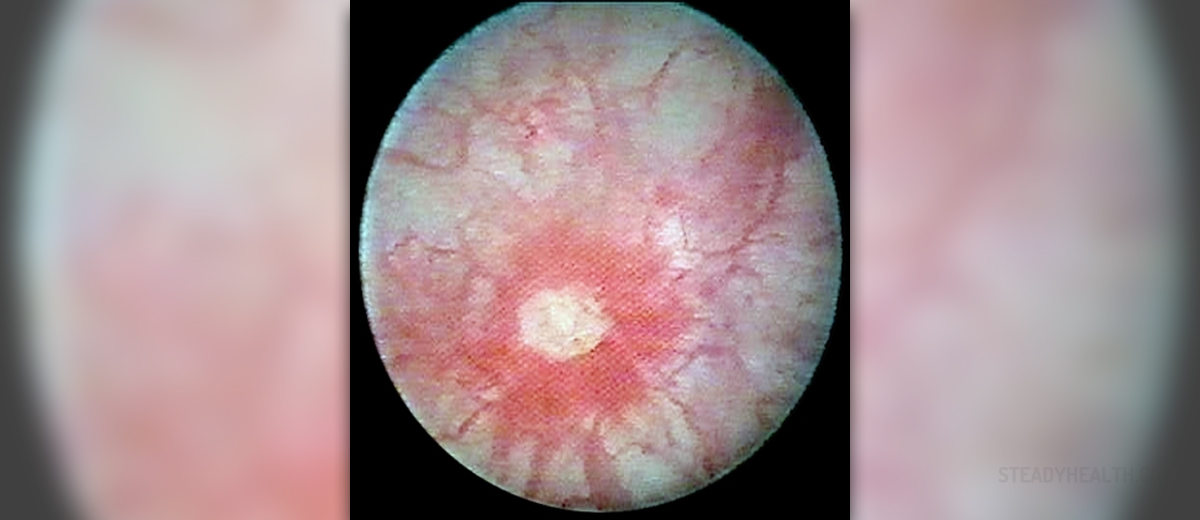
Interstitial Cystitis - Introduction
Interstitial cystitis is a chronic inflammation of the urinary bladder which typically features with characteristic pain associated with urination, frequent urinating, urgency to urinate and pressure inside the bladder or pelvis. The pain in interstitial cystitis seems to worsen with certain foods or drinks. The filling of the bladder intensifies the pain while alleviation is achieved after urination. Apart from the previously mentioned, patients suffering from interstitial cystitis may also complain about nocturia, pelvic floor dysfunction and tension, painful sexual intercourse etc.
This medical condition affects both genders and people of all ages. It was earlier associated with menopausal women. However, since there is an evident rise in number of male patients suffering from interstitial cystitis it simply cannot be associated only with female patients. But it is still more frequent among women.
Symptoms of Interstitial Cystitis
The symptoms of interstitial cystitis are not the same in all patients and may vary in characteristic, severity and duration. There are different combinations of the symptoms and they may even change throughout the day. Some of the most frequent symptoms of interstitial cystitis are persistent and urgent need to urinate, frequent urination of small amounts of urine, pelvic pain, pressure in the bladder or pelvis, pain between the vagina and anus in women, pain between the scrotum and anus in men, painful intercourse, burning sensation while urinating, blood in urine and cloudy or smelly urine.
Diagnosing Interstitial Cystitis
Setting of the definitive diagnosis can be rather challenging and it usually takes some time. This can be easily explained by the fact that symptoms of interstitial cystitis resemble those which are typical for urinate tract infections.
The patients can help in setting of the diagnosis by keeping a diary and recording all the symptoms, their occurrence, length and severity. Also patients need to report what foods they have consumed and if they have taken any medications.
After having a conversation with the patient the doctor performs physical examination and additional tests and examinations including urinanalysis, ultrasound of the urinary tract, cystoscopy, bladder wall biopsy, bladder capacity test, and urethral biopsy.
Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis
Patients suffering from interstitial cystitis usually require a combination of treatment modalities. Oral medications prescribed to these patients include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, tricyclic antidepressants and antihistamines. Furthermore, the doctor is also allowed to prescribe pentosan, a medication approved by the Food and Drug Administration for people suffering from interstitial cystitis.
Additional treatment modalities include nerve stimulation, bladder distention, and application of specific medications inside the bladder (dimethyl sulfoxide or a solution which contains three medications: heparin, lidocaine and sodium bicarbonate).
And finally, the last treatment modality for patients suffering from interstitial cystitis is surgery. There are several surgical procedures which are performed only in patients with severe pain and whose bladder can hold only small amount of urine. Surgery for interstitial cystitis includes bladder augmentation, fulguration and resection.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...