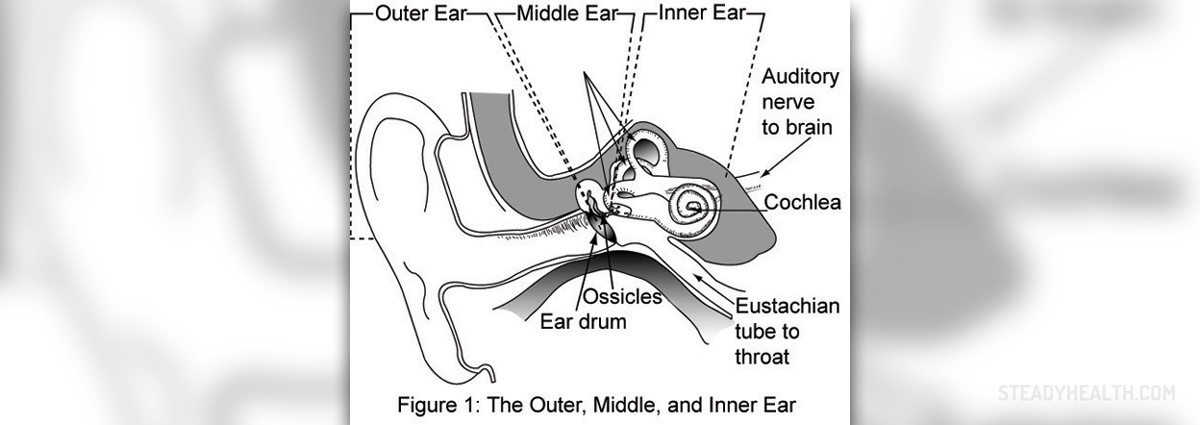
What is vestibular neuritis?
The inner ear is transmitting signals to the brain through the vestibulo - cochlear nerve. If this nerve gets inflamed, it may cause feelings of nausea, dizziness, and imbalance. This condition is known as vestibular neuritis. In most cases, only one ear is affected by vestibular neuritis.
Symptoms
Dizziness related to some problem in the inner ear such as vestibular neuritis frequently comes out of nowhere, but it is also common to experience dizziness immediately after a person wakes up in the morning. Symptoms related to vestibular neuritis such as an intense vertigo may last for days on end. Other symptoms related to vestibular neuritis include vomiting and nausea, imbalance (which causes problems when sitting, standing and walking) and difficulty in concentrating. If hearing problems such as a buzzing in the ears or a hearing loss are experienced alongside these symptoms, than it might be a condition known as labyrinthit is.
Causes
This condition usually emerges after a viral infection such as flu or a cold, so viruses are usually blamed for causing vestibular neuritis. Still, some people are affected by vestibular neuritis, but had neither flu nor a cold, so there other causes of vestibular neuritis other than viruses. Symptoms that affected persons experience are caused by the 'wrong' signals that are being sent to the brain by the inflamed and swollen nerve. 'Wrong' signals tell the brain that the body is moving even when it is not. So, on one end, brain is told that there is movement. Meanwhile, input from the eyes tells the brain that the body is not moving – or that it is moving in another direction. These signals are contradictory and confuse the brain, causing imbalance and sensation of dizziness – it seems that the space around the person is spinning.
Diagnosis and treatment
Medical assistance should be sought as soon as you experience the described symptoms. Diagnosis is based on looking at the symptoms and MRI scan and examination of the patients' eye movements if the symptoms are not conclusive. Primary form of treatment is a couple of days of complete rest in bed, and it is advised to keep the head as still as possible or at least to avoid any quick or sudden head movements. Balance exercises are used in order to learn to control the symptoms. Medications such as antihistamines or corticosteroids might soothe the inflammation and the doctor might recommend their use. The inflammation usually resolves within a few weeks and there is rarely any permanent damage. If the symptoms last for months then the patient must undergo a process known as compensation. This includes vestibular rehabilitation exercises, which help the brain to adjust to to the fake imbalance sensation.









_f_280x120.jpg)
_f_280x120.jpg)





Your thoughts on this
Loading...