
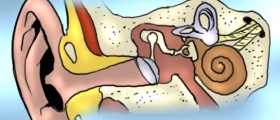
A vestibular disorder is the one affecting the vestibular system, an integral part of a rather complex system in charge of maintaining balance. Namely, balance is something that results from proper functioning of several systems including the visual system, vestibular system and proprioreception. So, practically damage to any of the mentioned systems may affect balance and trigger its deficits.
Vestibular System Function
As previously mentioned the vestibular system together with our eyes and proprioreceptors located in out skeletal system maintains the position of our body. This refers to rest as well as motion. What is more the mutual connection and cooperation between these systems is essential for maintaining a steady focus on some object although our body might be moving. This is achieved by detection of mechanical forces one of which is gravity.
The vestibular system comprises the semicircular canals and otolithic organs. We have three semicircular canals filled with fluid. They are arranged in such a way so that each of them is at right angle to the next two. Inside each canal there is a specific structure that resembles a raindrop. It is filled with a gel-like substance, the one playing major role in detection of one's position. The canals also contain specific hair cells called stereocilia. These are in a close contact with the gel i.e. they extend into the gel. When we move our head, the gel moves as well and stimulates the stereocilia which results in sending information to the brain. After signals have been processes the brain realizes the exact position of our head.
Otolithic organs are settled between the cochlea and the semicircular canals. There are the utricle and saccule. These organs inform the brain when we move from the front to the back and vice versa. They also provide information about whether we are sitting, lying or leaning back. The utricle and saccule also contain gel and stereocilia. They additionally comprise tiny little grains made of calcium carbonate known as otoconia. When our head moves, these grains move along and stimulate streocilia, triggering signals that once again reach the brain and inform it about the position of our head.
All in all, this is a very important system and any damage to it can trigger various health issues some of which are, unfortunately, incurable.
Why do Balance Disorders Occur?
There is a range of potential underlying causes of balance disorders. Some of them are ear infections, head injury/trauma, circulation disorders affecting the ear or the brain etc. Furthermore, intake of some drugs may be blamed for specific changes in the vestibular system and cause problems with balance. Changes in the vision along with problems regarding skeletal system may contribute to the disorder too.
It is normal to experience some balance issues once the person gets older. However, even young adults or children may be affected by this health problem.
There are many different balance problems. The most frequently reported ones are benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), labyrinthitis, Ménière's disease, perilymph fistula and mal de debarquement syndrome (MdDS).
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo occurs as a result of dislodgement of otoconia from the utricle (where they are normally found) into the semicircular canals. It is characterized by brief episodes of vertigo once the head is moved in a specific direction. Labyrinthitis is inflammation of the inner ear always accompanied by dizziness and lack of balance. In Ménière's disease patients are affected by hearing loss, repeated episodes of vertigo and tinnitus. The underlying cause remains unknown. Perilymph fistula is the term for leakage of fluid from the inner into the middle ear. As a result patients experience dizziness, nausea and may feel unsteady when walking or standing. Finally, Mal de debarquement syndrome (MdDS) typically develops after some kind of movement like a cruise or aircraft flight. People affected report a persistent sensation of motion in the form of rocking, bobbing or swaying.
Therapy for Vestibular Disorders
Vestibular rehabilitation therapy is a successful treatment approach for many deficits that affect the inner ear, to be more precise the vestibular system. It actually promotes compensation for lost function why is achieved by better central nervous system coordination. Almost all of the aforementioned conditions can be successfully treated with vestibular rehabilitation therapy.
Before engaging in this type of therapy patients undergo thorough evaluation by a well experienced physical and/or occupational therapist. One of the tests these professionals regularly perform is the eye-hand coordination test. After examination, they create a specific and unique treatment plan, based on individuals needs of the patient. The goal of the treatment is to help the brain to recognize signals obtained from the vestibular system and coordinate these with signals obtained from the eyes and skeletal system.
The program is efficient and help the vestibular system to neglect the movements that actually provoke symptoms. The exercises can be easily performed at home after initially being performed with the assistance of the therapist.
Finally, the results of such therapy are more than successful, therefore it is highly recommended by many medical experts.







_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...