When a person feels dizzy, they are disoriented and feel as though they or their surroundings are moving. In severe cases, a person may faint. If a person experiences such extreme dizziness frequently, it indicates some underlying condition that has to be identified. Extreme dizziness may result from several causes, such as vertigo, sugar levels in the blood, low blood pressure, panic attacks, poor nutrition and dehydration, or pregnancy.
Vertigo
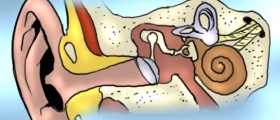
Vertigo occurs due to a problem in the brain (central vertigo) or the inner ear (peripheral vertigo). Peripheral vertigo can be caused by viral or bacterial infection of the inner ear. The vestibular system represents structures in the inner ear, and it includes the cochlea, a small chamber inside the inner ear that contains cochlear fluid. When infections spread onto cochlear fluid, the nearby nerve, called the vestibular nerve cannot send proper signals to the brain. Due to these wrong signals, a person can feel confused, disoriented, and lose his or her balance. Problems with the vestibular system can be treated with vestibular rehabilitation therapy that can reduce dizziness.

Blood Sugar Levels
Normal blood sugar levels range between 70 and 150 mg. Typically, blood sugar levels are lower in the morning, which can lead to dizziness. However, chronic low levels of sugar (hypoglycemia) can cause fatigue, imbalance, and falling unconsciousness. Low oxygen levels in the blood can also result in dizziness.
Low Blood Pressure
Generally, low blood pressure is often associated with dizziness. Low blood pressure causes syncope and a feeling of dizziness that occurs due to sudden changes in body positions. This occurs due to an insufficient supply of oxygen to the brain because the heart requires more time to send the blood to the brain. Low blood pressure has to be treated with proper medications to minimize the dizziness.
Panic Attacks
Dizziness may occur due to certain mental states like depression or anxiety. Anxiety is characterized by panic attacks which is an episode of intense fear. Panic attacks result in physical reactions such as irregular heartbeat that can lead to dizziness. The person who experiences panic attacks also has breathing rhythm affected. Panic attack may cause shortness of breath or hyperventilation and it is recommended to do deep breathing and other relaxation techniques in such cases to relieve the dizziness.
Diet
Irregular eating and consuming unhealthy foods can cause vomiting, weakness, and extreme dizziness. Dizziness may also occur due to insufficient fluid intake. If dizziness is caused by dehydration it can diminish after you increase your intake of water.
Pregnancy
Hormonal changes during pregnancy often lead to extreme dizziness. This occurs because hormones contribute widening of blood vessels to ensure adequate blood flow to the fetus while the return of the blood to the mother is decreased. This can result in low blood pressure that triggers dizziness.
- In this cross-sectional study, we investigated the 1-year prevalence and related factors in the general population with an experience of chronic dizziness.
- This study analyzed persons (n = 5,163) who respond to dizziness and nutrition questionnaire from participant of Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES, 2019-2020).
- Of individuals over 40 years, 25.3% of the general population (61.6% females) reported either dizziness or imbalance for the past year. Moreover, 4.8% of the patients reported they suffered from chronic dizziness or imbalance for more than 3 months. In multiple regression analysis, patients with chronic dizziness were older, females, had lower body mass index (BMI), had stress awareness, and had a history of tinnitus within 1 year (>5 min per episode).
- Relative to normal body weight, both overweight and mild obesity (obesity stages 1 and 2) were associated with a significantly lower risk of chronic dizziness. Overweight, obesity stage 1, and obesity stage 2 had odds ratios of 0.549 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.332–0.910], 0.445 (95% CI, 0.273–0.727), and 0.234 (95% CI, 0.070–0.779), respectively.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...