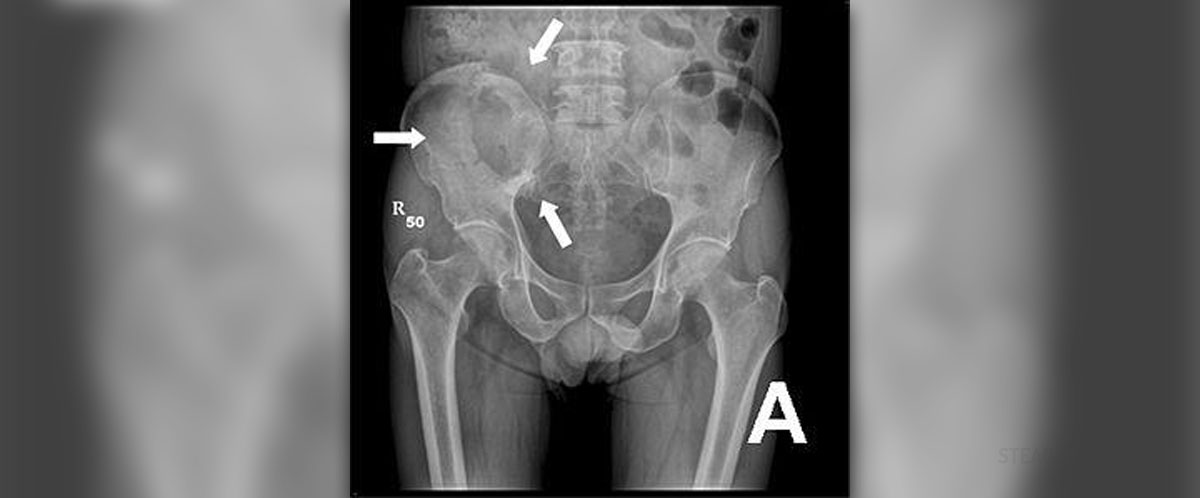
Radiography is a procedure during which X-rays are used for observing the inside of the human body. The image received through this procedure displays different parts of density and composition, allowing health experts to differentiate between bones, soft and hard tissue, diagnosing illnesses and monitoring one's health.
Even though the most commonly used X-ray imaging provides health experts with 2D images, new technology has surpassed this and is capable of producing full 3D scans in very high detail, enhancing the purpose of radiography even more.
Where is Radiography Used?
Basically, this form of scanning is used for many different situations, whenever a the visualization of one's internal body parts is necessary. Hence, the usages are many, ranging from diagnosing specific medical conditions to planning a future radiation therapy treatment.
The whole procedure involves exposing the human body to X-rays which penetrate it and pass through it. This whole process is recorded and an image is produced. Due to the fact that X-rays scatter once they hit different structures, a detector records this and creates an image.
Therefore, radiography is a basic part of dentistry, since it can be used for obtaining images of the inside of one's teeth. Also, X-ray imaging can help surgeons and other medical staff members in the process of verification of correct placement of surgical markers before any invasive procedures take place.
Furthermore, mammography is carried out through a special radiography procedure and any orthopedic evaluations need X-ray scanning too. Additionally, spot film or static recording, being crucial parts of fluoroscopy are done this way, along with many types of chiropractic examinations.
Even though the benefits of radiography surpass the potential adverse effects it may cause, the dangers related to this form of exposure exist nevertheless. Some of the most severe side-effects possible are development of cancer due to radiation exposure or formation of cataracts later in life. Also, pregnant women may want to avoid radiography procedures due to the fact that these might cause problems in the growth and development of the fetus.
However, taking into consideration that the chances of developing cancer due to radiography exposure are quite small, even ignorable once compared to the positive effects of these procedures, radiography is a crucial part of medicine. Yet, bear in mind that the frequency of one's exposure to X-rays should be limited.
What is Radiographer's Occupation?
Being a radiographer mainly involves working in radiography and imaging departments of hospitals, even though these professionals may work in clinics or surgical departments too.
A radiographer does not perform only one type of scanning. Rather, he/she should be skilled in ultrasound, MRI, nuclear medicine and X-rays. Radiographers involved in diagnostic parts of medical facilities are people who have the most work on their hands. Yet, if you desire to become specialized for just a single type of radiography, the expertise of yours is bound to become narrower.
In general, a radiographer is considered to be capable and qualified for carrying out X-ray scans, examining people's bones and cavities, as well as any foreign objects present in their bodies. Also, he/she is considered to be an expert in fluoroscopy, delivering real-time images of one's digestive system, CT scanning, resulting in images of specific slices of body parts, MRI scanning, producing either 2D or 3D images of certain sections of the body, as well as ultrasound, mostly used in gynecology, obstetrics and heart examinations.
Finally, a person in charge of radiography is supposed to carry out angiography, examining one's blood vessels.
Naturally, collaboration and cooperation with other health expert within the medical facility is a basic characteristic of a radiographer's profession. Furthermore, a radiographer is constantly facing improvement and profession modifications, moving on to being involved in management, researches, clinical trials or even teaching.
Some radiographers have specialized for working with cancer patients, along with all the health experts who are providing medical care for these people. Here, a radiographer is supposed to emit adequate doses of ionizing radiation onto specific parts of the patient's body, attacking the tumors and helping the patients battle this cruel disease.
Those radiographers who use ultrasound devices in hospitals may help in treatment of babies, chiildren or adults. However, in order to handle ultrasound and sonography devices, one needs to meet all the clinical and academic requirements.
Therefore, a job of a radiographer is quite a diverse one, depending on his/her qualifications and the facility he/she is a part of. Nevertheless, radiography is a very important part of any health institution. Subsequently, these people are invaluable members of health providers.
To sum up, there are numerous radiography procedures available, from ultrasounds to X-ray, CT and MRI scans. Hence, radiographers need to be highly qualified for handling the devices and carrying out the procedures necessary for these types of exposure, regardless whether diagnosis or treatment is in question.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...