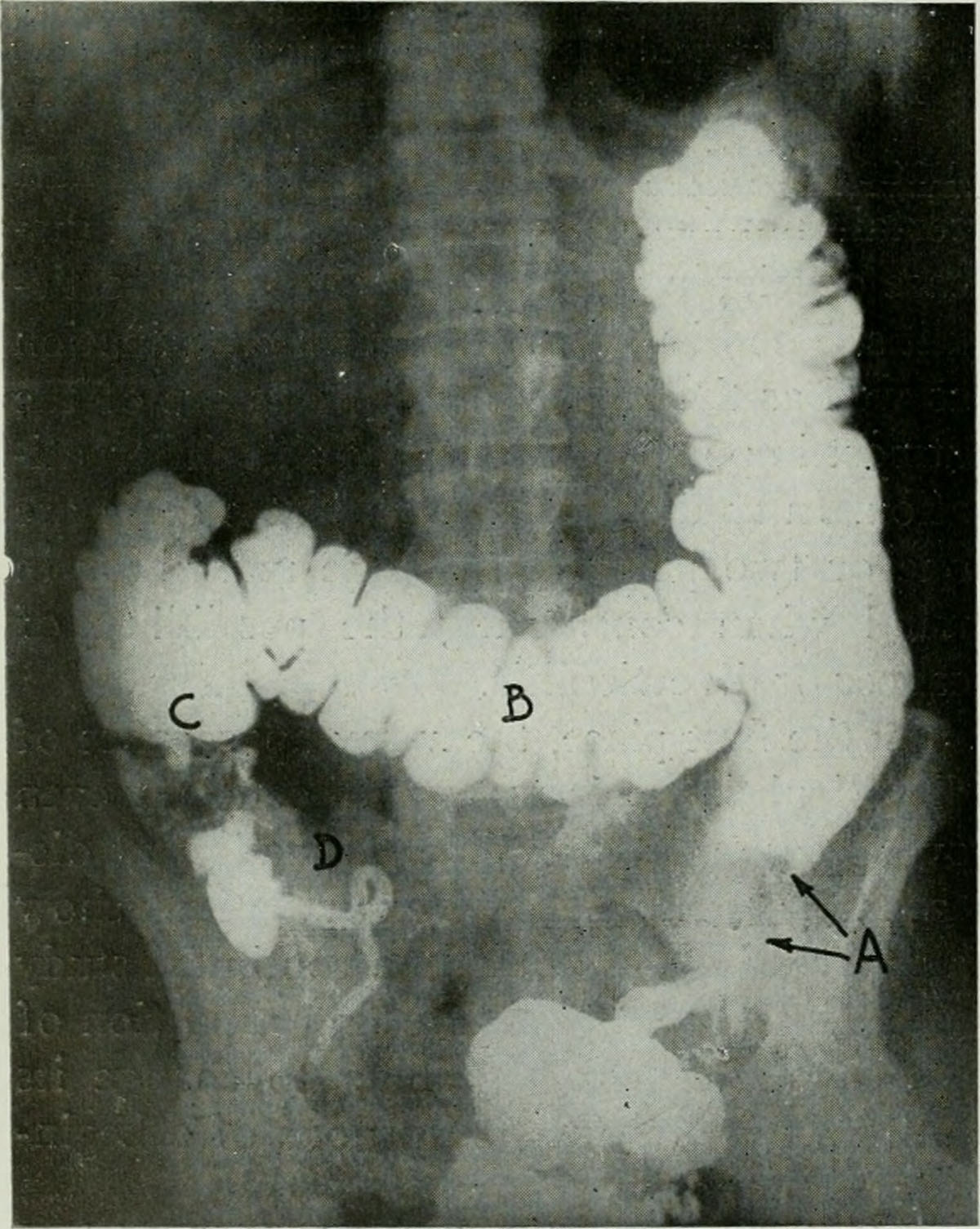
Inflammation of the Colon
The colon and the rectum are the most important parts of the large intestine. The colon absorbs the water and passes all food particles that remain undigested to the terminal part of the large intestine, where it is stored in the form of feces. Feces are removed through the organism through the anal orifice in the form of stools. If there is a swelling of the outer lining of the colon, then such a condition is known as colitis, or inflammation of the colon. If the colon becomes inflated at some places, it is likely that stomach ulcers will be developed. This condition is referred to as ulcerative colitis.
It is possible to draw a comparison between the colon and a water-carrying pipe. Any obstruction in the pipe will prevent the flow of water, and the pipes need to be cleaned regularly. Our colon requires the same, that is, it requires periodical cleaning. If there is an ongoing inflammation in the colon, then the its outer walls become thin and porous and some of the harmful or toxic waste, residues from the process of digestion, can escape into the body through these weakened walls. Such escaped waste can deposit in tissues all over the organism. Problems caused by such runaway toxins include destruction of cells, irregular digestion or problems related to bowel movement.
Causes
Honestly,science still does not have the answer to what causes colon inflammation. According to what is currently known about how a human body works, the most likely cause of colon inflammation appears to be the unwanted and unnecessary activation of the immune system in the intestine. Under normal circumstances, the immune system produces proteins known as antibodies, whose role is to fight off any unfriendly bacteria or virus that causes diseases. Once that particular threat is dealt with, the immune system ceases production of antibodies. However, the immune system can produce antibodies without a cause, and this seems to be causing the inflammation of the colon.
Some bacteria and viruses which produce toxins that cause cells of the colon to secrete certain salts which cause colon inflammation of the colon. It is still unknown which type of bacteria or viruses cause thiscondition.
Symptoms
Inflammation of the colon effects bowel movements. Symptoms include long periods of diarrhea or constipation, painful passing of the stool or blood in the stool, abdominal pain or problems with gas. Other telltale symptoms are chronic vomiting and nausea, weight loss, lack or loss of appetite and constant fatigue.
TreatmentTreatment mostly depends on the scale of the inflammation and will vary from person to person. Medicines serve to minimize the effects of the inflammation. Surgery is suggested, if there is no improvement and the inflammation remains unchecked. Surgery consists of removing the blockage in the colon and rectum, by bypassing or removing the rectum. The patient can lead a normal active life after the surgery.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...