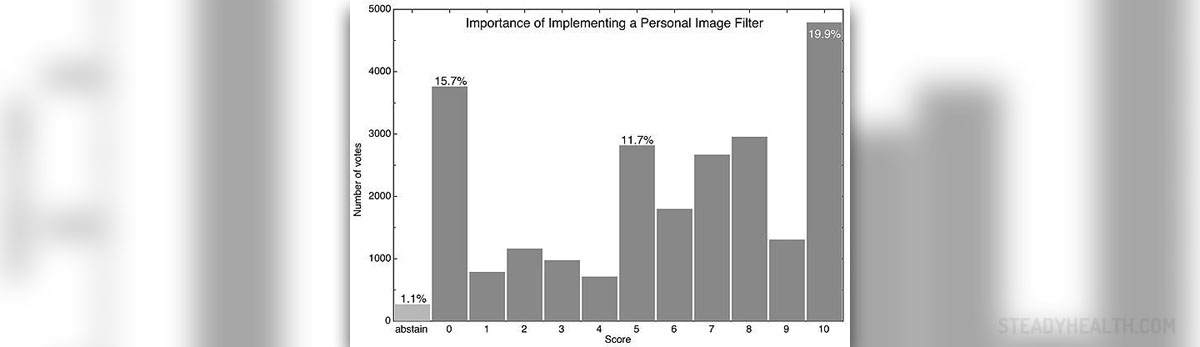
Reproductive health or sexual health and hygiene address the reproductive processes, functions and reproductive system at all stages of women’s life. Women's reproductive health applies that she is able to have a responsible, satisfying and safe sexual life, and to reproduce at full freedom. Sexual health is very important for both sexes but when applied on women it includes the access to access to appropriate health care services and ability to go safely through pregnancy and childbirth. However, sexual health is not only defined as the absence of disease, but also positive and respectful approach to sexuality, access to information and safe, effective, affordable and acceptable methods of birth control.
Women’s reproductive health
Women’s reproductive health focuses on protection of women’s reproductive system and research on fertility, infertility, contraception, and sexually transmitted diseases. Women’s reproductive system is one of the most fragile body systems, prone to many infections and injuries. Problems in reproductive health account for 20% of all health problems of women, globally. Women should pay special care to their reproductive systems, especially if they are planning to have children. Some of the most common diseases, that may cause irreversible damage to reproductive health, usually begin with no signs of infection or disease. Protecting the reproductive system includes regular controls and exchange of the information with medical professionals.
Common threats to women’s reproductive health
Bacterial vaginosis is one of the most common dangers for women’s reproductive health. It is usually sexually transmitted but even women who have never had sexual intercourse may become affected. In some cases it may not even have any symptoms, but it makes women more vulnerable to other sexually transmitted diseases. It is especially dangerous for pregnant women, since it causes premature delivery and low birth-weight babies.
Chlamydia is the most commonly diagnosed sexually transmitted disease in the United States. It has no symptoms but severely affects a woman’s ability to become pregnant and have children, if left untreated.
People who already have a sexually transmitted disease are more likely to become infected with HIV. To reduce the risk HIV and achieve maximum protective effect, couples should use condoms that act as a barrier for blood, or semen, or vaginal fluids, and helping to keep them from passing from one person to the other during sexual intercourse.
Genital herpes is a widespread and highly contagious infection that affects both males and females. It is caused by herpes simplex virus 2. About 16% of Americans have HSV-2 infections and for about 75% to 90% of these individuals, genital herpes is completely asymptomatic. Even though they have no sign of infection, these individuals may easily infect their sex partners 10% of the time.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...