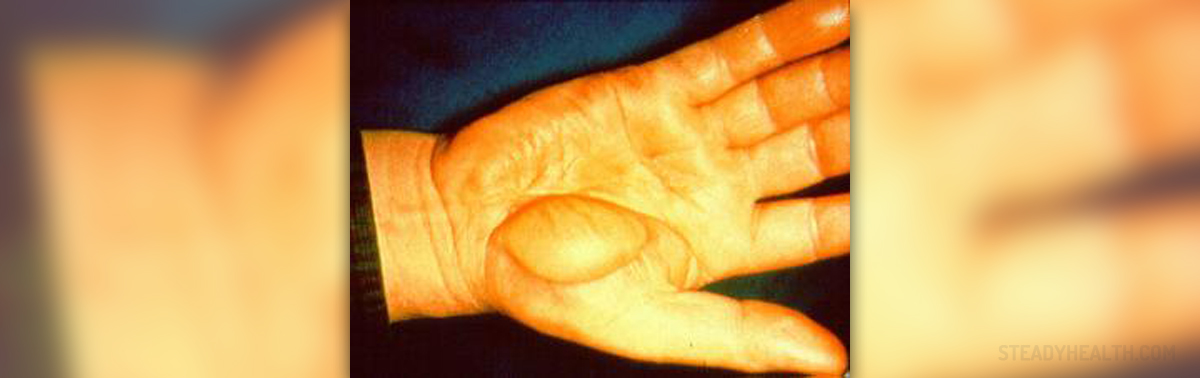
Electrical burns are caused by electricity passing through a person's body, after being in contact with sources of electricity. There are three degrees of burns, the third-degree being the most dangerous and severe. The degrees depend on the amount of electricity a body has been exposed to and on the duration of the exposure.
It is essential to know the difference between the degrees of a burn. In the case of a first-degree burn, the skin will be red and painful, and the burn will affect only the upper layer of the skin. Unless there are complications, this kind of burn does not require medical treatment.
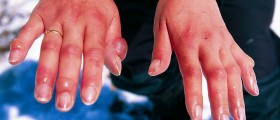
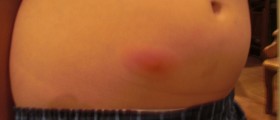
Second-degree burns are more severe, as they affect more layers of the skin. They are very painful, with blisters and more redness occurring. If a larger area is affected, a doctor should be consulted.
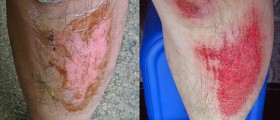
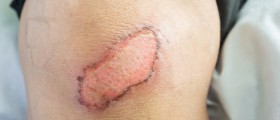
Third-degree burns, however, need immediate medical assistance, since they are the most severe. They affect all layers of the skin and the skin becomes dark, almost black, and flaky.
It is important not no touch the burn victim unless it is absolutely safe to do so, because the electricity can pass from one person to another through physical contact.
The first thing to do is to make sure that the source of electricity has been shut off and then move the victim away from it, being careful to use only items that are not conductors for electricity, such as wood and textiles. Medical assistance should be requested immediately, providing the emergency medical responders with information about the burn - its extent and the circumstances under which it occurred.
The electric shock can also affect internal organs, causing serious damage to the individual. Therefore, the next step is to check the victim’s pulse and breathing and to perform CPR if necessary. The victim should then be checked for symptoms of shock such as cold skin, paleness, and a high heart rate (>100). Emergency treatment of the wounds is to be done with clean, dry bandages, avoiding contact between the wound and unclean materials and hands . If there are pieces of clothing stuck to the wound, they are not to be removed. Wounds should not be treated with water, ice, or oil.
In case of more mild burns, the affected area should be treated with cold water, but not with ice. After cleaning the area with soap and water and pat-drying it with a clean towel, the wound should be covered with bandages, checking every now and then for possible infections. Painkillers such as ibuprofen can be used to relieve the pain. Additionally, topical anitobotics such as Polysporin can be applied.
Electrical appliances and installations should be handled with caution and there should always be a fire extinguisher nearby at all times.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...