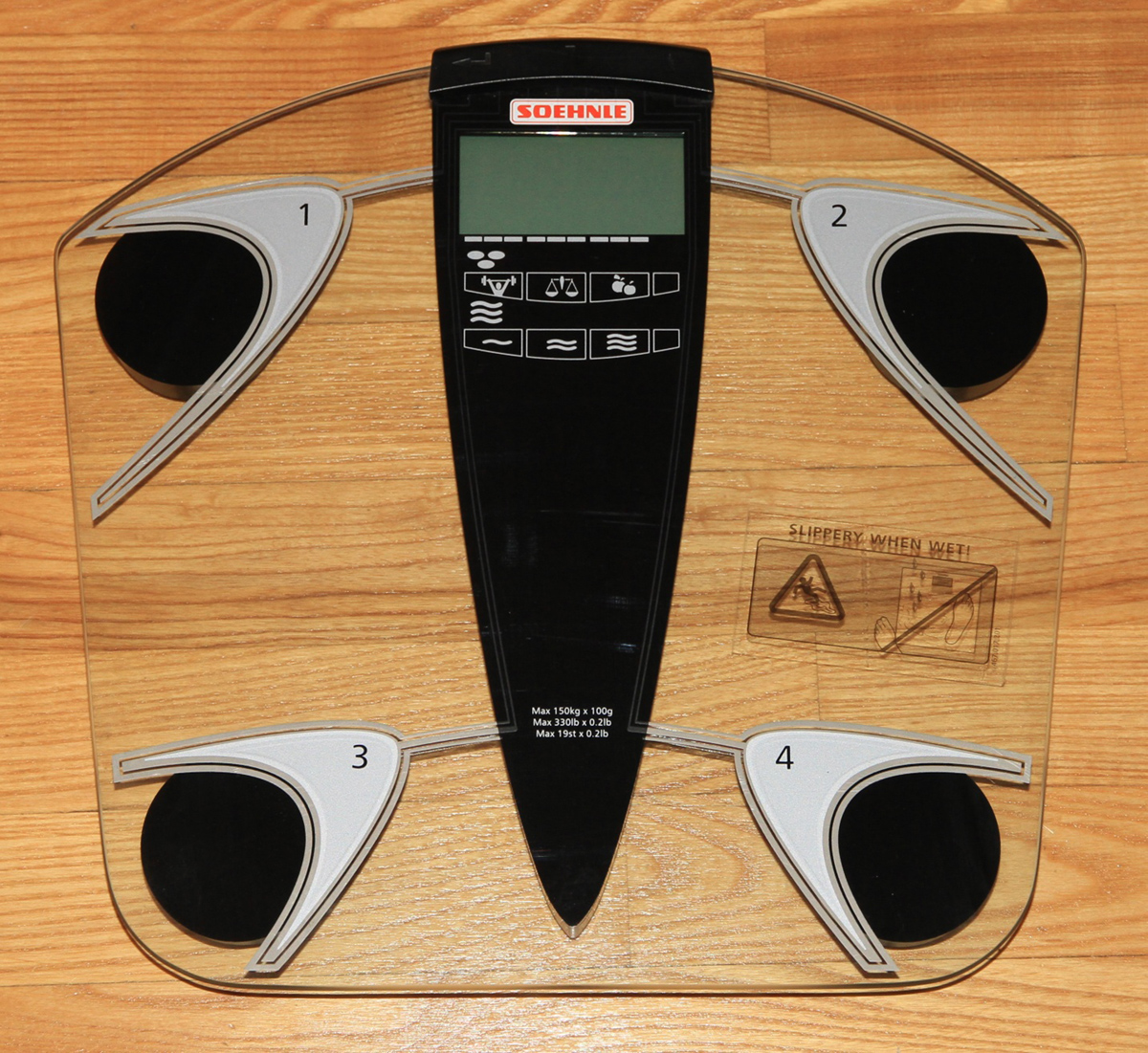

Often, merely measuring the weight of an individual will not be enough to give an indication of that person’s overall health. This is because weight does not identify the actual composition of the body; muscle versus fat. Thus, measuring body fat becomes important, as it indicates not just one’s level of fitness but also whether one might experience any future health risks. Higher body fat means a higher risk for health problems. Obesity can lead to problems like heart disease, infertility, depression, diabetes, stroke, sleep apnea and skin problems.
Several different methods of measuring body fat exist, and some ways are simpler than others. Some methods, like the skinfold test and bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), can be done at home, with the right equipment. Others, like dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) normally require the presence of a doctor.
Skinfold Test
The skinfold test uses calipers to measure fat at various locations on the body. The types of calipers used are digital skinfold calipers and manual skinfold calipers. Some digital calipers may have the capability to give an instant fat percentage without the need for chart consultation. Using the calipers, the following areas are measured for thickness: triceps, subscapular, thigh, abdomen, supra iliac, mid-auxiliary and the chest. The advantage of this approach is that the calipers are relatively cheap and the process is quite simple. However, the possibility of inaccurate measurements being registered is quite high and the presence of someone else to actually take the measurements is required.
DXA
DXA is probably the best and most accurate way to measure body fat. It will produce results that are accurate to within 3 or 4%. This method can also be used for bone density measurement. Primarily, DXA uses x-rays to scan the body - one x-ray scans body tissue and the other cannot recognise body fat. These separate images are compared and thus body fat percentage is calculated. DXA is very accurate but expensive and must be performed in a hospital or laboratory.BIA and other tests
BIA utilises electric currents to measure the body. This current is passed through the body - the current penetrates muscle, tissue and fat at different speeds, and this is used to measure the density of the body. The BIA machine itself will calculate your body fat percentage to within 10-15% accuracy. These machines are used either at home or in a laboratory and the machines themselves are safe and easy to use. This approach can be cost effective and it can be done while alone. Some factors can have an influence on the accuracy of this method - women store fat on the hips rather than the abdomen and an individual’s level of hydration can also have an impact on the accuracy of the test. Different machines may also produce different results.
Another method, known as water weighing, might also be used. This method involves measuring water displacement after a subject is submerged in water. This method can be accurate, but is normally only performed in research facilities.



-Test-And-What-Do-The-Results-Mean_f_280x120.jpg)










Your thoughts on this
Loading...