People suffering from Fanconi anemia are actually born with this disease and most of them show signs of this genetic disorder at birth. Still, some patients may not be diagnosed at birth but after some time, once the disease leads to typical abnormalities regarding function of certain organs in the body. So, in case the condition is not diagnosed at birth, it is most commonly identified between the age of 2 and 15.Diagnosing Fanconi Anemia
The condition can be confirmed with the assistance of symptoms and signs as well as after taking patient's medical and family history. Definitive confirmation is achieved by genetic testing.
Geneticists are, therefore, doctors who are commonly involved in diagnosing Fanconi anemia. Obstetricians may detect and report birth defects and other malfunctions of organs and organ systems these patients may be suffering from. Additional help is obtained from a hematologist who is in charge of blood abnormalities associated with the condition.
As far as family history is concerned, since this is an inherited disease, it is usually reported in other family members as well. Parents do not have to suffer from Fanconi anemia but they need to be carriers of the defective gene and transmit the gene to their child who may become a carrier or develop the disease.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Symptoms and signs of Fanconi anemia are not unique and may also be reported in people suffering from other diseases. The only way to confirm the condition is by performing certain genetic tests.
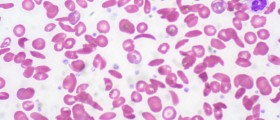
Chromosome breakage test is most commonly performed test for the purpose of confirmation of the disease. The test is only done in special laboratories and shows whether the patient's chromosomes are prone to break.
Cytometric flow analysis is another test which uses chemicals to check whether the chromosomes are affected as cells grow and develop and how.
Mutation screening checks whether there is a mutation/mutations in patient's genes associated with Fanconi anemia.
Diagnosing Fanconi Anemia before Birth and at Birth
Before birth the baby can be easily tested with the assistance of amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS). While amniocentesis is performed between 15th and 18th week of pregnancy, chorionic villus sampling may be done before, between 10th and 12th weeks of pregnancy.
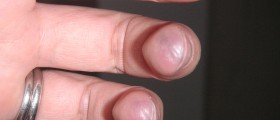
Some babies are born with defects characteristic for Fanconi anemia. These include missing and oddly shaped thumbs, poorly developed/missing bones in the arms, deformities of hips, legs, hands and toes as well as scoliosis. Furthermore, there may be skin discoloration, missing or misshaped kidneys and congenital heart defects. Mental retardation and digestive issues are also common for patients suffering from Fanconi anemia.
Fanconi Anemia in Childhood and Later in Life
Some patients have no birth defects. They are usually diagnosed with Fanconi anemia once problems with the bone marrow (aplastic anemia) occur. The condition can be also diagnosed if patients develop cancers that are not characteristic for their age.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...