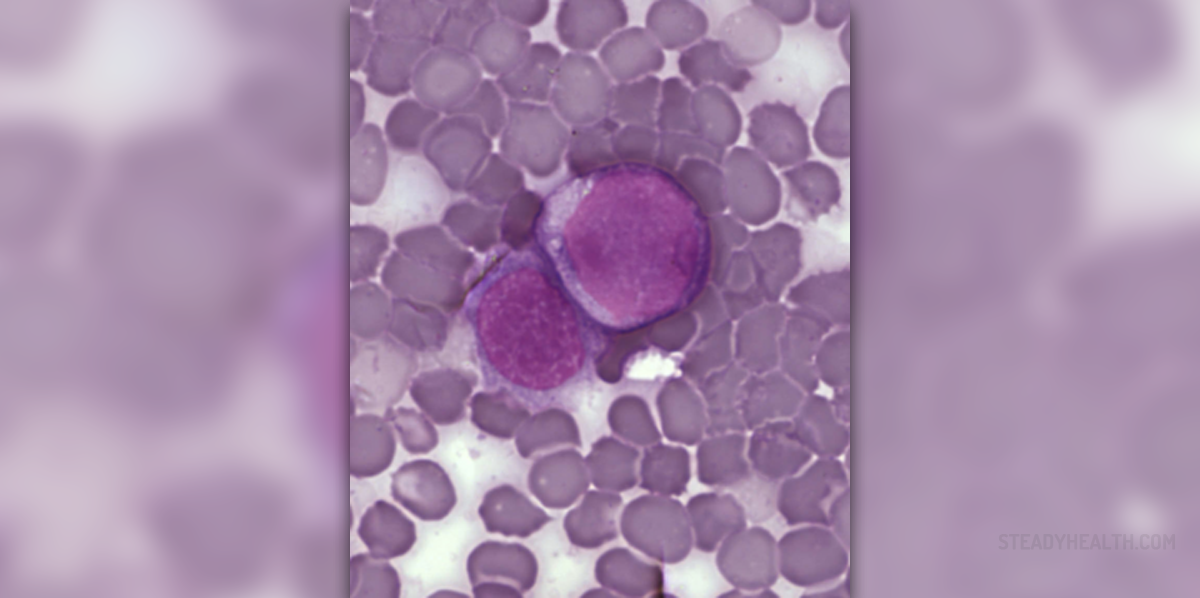
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is only one type of leukemia, a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. The very term chronic refers to the fact that this type of leukemia progresses more slowly comparing to other types of leukemia. It is estimated that each year approximately 15.000 people in the Unites States are diagnosed with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
There are certain factors which may contribute to the occurrence of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. They include patient's age, gender and race. Namely, chronic lymphocytic leukemia is usually diagnosed in people who are over 50. Furthermore, men are more prone to this type of leukemia comparing to women. And finally, white people are the most susceptible race to chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Apart from the previously mentioned this type of cancer affects people who have had family history of blood and bone marrow cancers and it is also common for people exposed to certain herbicides and insecticides.
Symptoms of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
The disease may be asymptomatic and once the symptoms fully develop they include fatigue, fever, night sweats, weight loss, frequent infections, enlarged and painless lymph nodes.
People suffering from this type of leukemia are highly susceptible to infections, particularly infections of the upper and lower respiratory tract. They are also prone to other cancers such as Kaposi's sarcoma, melanoma, bladder, lung and stomach cancer. One more problem of chronic lymphocytic leukemia is that it may switch to more aggressive form of the disease called large B-cell lymphoma.
Diagnosing Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Patients suffering from chronic lymphocytic leukemia undergo several diagnostic tests. A complete blood count gives insight in the number of lymphocytes in a blood sample. It is essential to determinate the type of lymphocytes involved. A specific test called flow cytometry or immunophenotyping is very effective in making a differential diagnosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and other body's reactions such as infection.
Additional test includes fluorescence in situ hybridization which is an analysis for genetic abnormalities, bone marrow biopsy and/ or aspiration and computerized tomography (CT). According to all the obtained data the doctor stages the disease.
Treatment for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
The stage of leukemia as well as the overall health of a patient determines the treatment. The treatment does not have to start in early stages of the disease. These patients are carefully monitored and the treatment will start once the disease starts to progress.
Intermediate and advanced stages of chronic lymphocytic leukemia are treated with chemotherapy, target drug therapy and bone marrow stem cell transplant.
There are also clinical trials which test new treatments as well as new ways of using already existing treatments. Unfortunately, clinical trials cannot guarantee a cure.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...