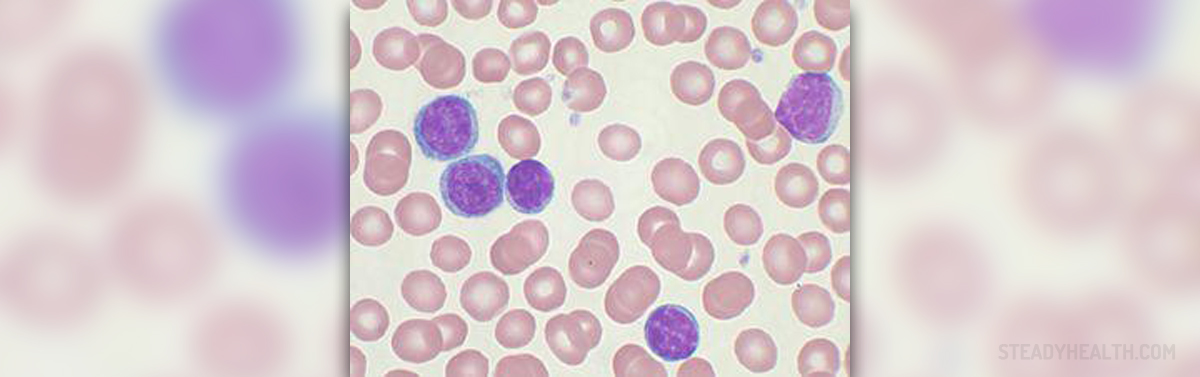
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is only one type of a malignant disease which affects white blood cells resulting in excessive production of these cells.
Causes of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is characterized by increased number and rapid proliferation of immature white blood cells (B lymphocytes) in the bone marrow. These tumor cells spread from the bone marrow and affect different lymphoid organs and tissues in the body. The effects are detrimental and a patient ends with low blood counts and weak immune system.
The actual cause of this type of leukemia remains unknown. This malignant disease does not develop due to previous exposure to radiation nor is related to cancer-causing chemicals and viruses.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia generally affects adult individuals and is rare in people younger than 40 years.Clinical Characteristics of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Symptoms and signs of this type of leukemia develop gradually and rather slowly. The condition is responsible for low blood counts and this subsequently leads to abnormal bleeding (insufficient number of platelets), frequent infections (lack of mature white blood cells) and anemia (insufficient amount of red blood cells). Furthermore, patients complain about fever and chills, fatigue, excessive sweating and night sweats. Loss of appetite and sudden weight loss are also typical for this malignant disease. And finally, there is enlargement of lymphatic organs (e.g. the spleen, liver, lymph nodes etc).Diagnosing Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
The first thing doctors do is taking patient's medical history and performing complete physical examination. What follows is blood testing. Patients suffering from chronic lymphocytic leukemia have abnormally high white blood cell count. They undergo aspiration or biopsy of the bone marrow and taking samples which are then pathohistologically examined. Additional test such as CT scan of the chest, abdomen and pelvis, flow cytometry, blood lactate dehydrogenase level and blood immunoglobulin level are necessary for proper staging. There are two staging systems, the Rai staging system and the Binet staging system.
Treatment for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
In early stages patients are only monitored. Treatment begins when infections start to occur frequently, the number of leukemia cells rapidly increases and there is significant drop in all three blood counts.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia requires aggressive treatment with several different chemotherapeutics. Most protocols include Fludarabine, chlorambucil, cyclophosphamide and rituximab. Alemtuzumab is administered in patients who do not respond to Fludarabine.
Relapse of the condition requires repeated treatment and sometimes administration of a newer drug called bendamustine.
Radiation therapy is not a part of the protocol but it may be used for painful and enlarged lymph nodes. Low platelets require blood transfusions. And finally, bone marrow or stem transplantation are recommended in younger patients in whom the disease has advanced.
- medlineplus.gov/chroniclymphocyticleukemia.html
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000532.htm
- Photo courtesy of Mary Ann Thompson by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Chronic_lymphocytic_leukemia.jpg














Your thoughts on this
Loading...