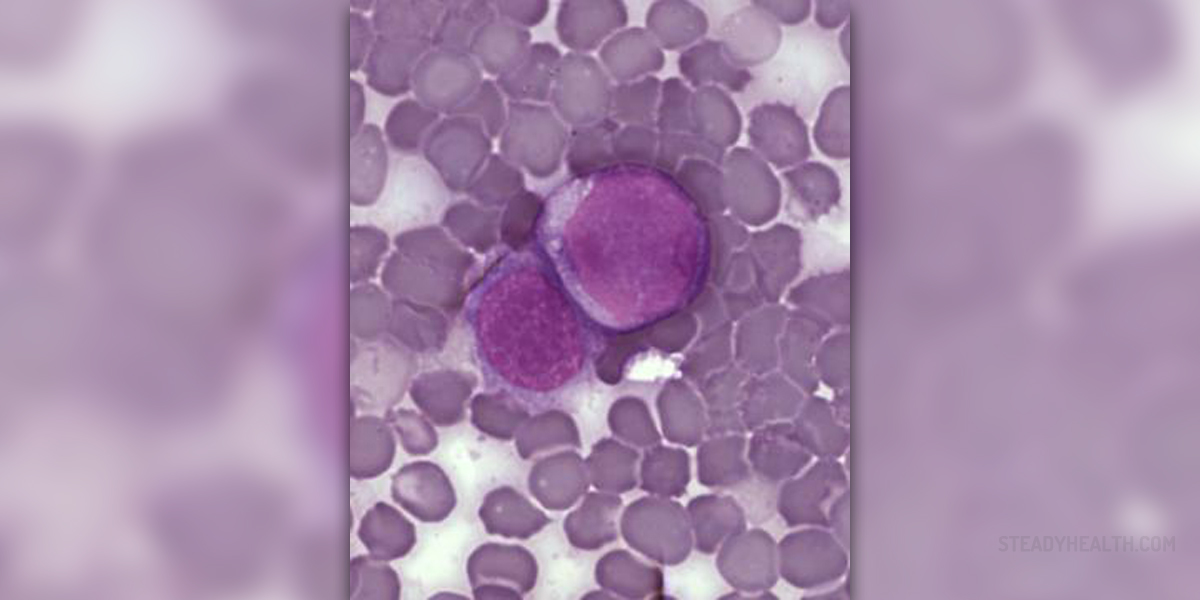
Cancer of the blood cells is known as leukemia. The bone marrow normally produces white and red blood cells and platelets, but in leukemia patients it starts to produce leukemia cells. These abnormal white blood cells do not function as normal white blood cells. They grow much faster and they do not stop growing after some time either. After certain time, there is much more leukemia cells than normal white blood cells and this provokes different medical problems.
Leukemia Types
Leukemia may be acute or chronic condition, depending on the progression of the illness. Acute leukemia is very fast and people are immediately sick, while chronic leukemia patients usually do not develop any symptoms for years, because the disease is progressing very slowly.
Another differentiation is based upon the blood cells leukemia affects. If the illness affects white blood cells – lymphocytes it is called lymphocytic or lymphoblastic leukemia. Myelogenous leukemia, on the other hand, affects different white blood cells, known as myelocytes.
So, there are 4 main types of this disease, being: acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) and also chronic types of these – chronic lymphoblastic and chronic myelogenous leukemias (CLL and CML). Children suffering from leukemia usually have ALL, AML or very rarely CLL. Adult leukemia patients mostly suffer from AML, CLL (especially people over 55 years of age) and CML.
Causes and Symptoms
Leukemia is still a mystery for doctors and scientists and they still cannot tell what is causing this disease. Identified risk factors include exposure to radiation or benzene at work. Smoking is also one of the factors which may contribute to the development of leukemia. Chemotherapy for cancer may also provoke leukemia, as well as some genetic disorders such as Down syndrome.
Some of the symptoms common for leukemia patients include headaches, fever and night sweats, bone or joint pains, easy bruising and bleeding and frequent infections. These patients may also experience swelling of lymph nodes and belly and abdominal pain or enlarged spleen. In many cases, patients do not feel hungry, start to lose weight and feel very weak and tired.
Treatment Options and Prevention of Leukemia
Acute leukemia requires urgent treatment to stop the growth of cancer cells. CLL patients do not require treatment unless showing some symptoms, while CML must be treated immediately. Acute leukemia is usually said to get into remission, because the disease might come back again. Chronic leukemia is mostly incurable and the treatment is helpful to manage the symptoms of the disease.
So far, there is no way to prevent development of leukemia. Even though there are some risk factors you should avoid, certain people get leukemia without being exposed to any of them. Also, there are others who have been exposed to these risks and still have not developed the disease.Avoiding high doses of radiation and toxic chemicals known to cause leukemia is the best course of action. Avoid using tobacco is helpful as well. For some people, avoiding cancer treatments that might lead to leukemia may also be an option.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...