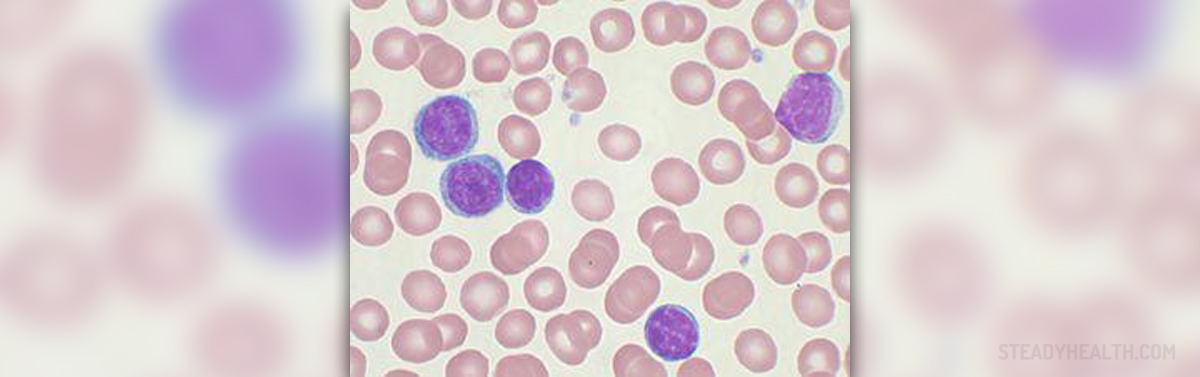
Leukemia is a cancer which may progress slowly and initially appears in the tissue which is involved in blood formation. There are two main types of leukemia, chronic lymphocytic and chronic myeloid leukemia. Both of these leukemia types predominantly affect adults, especially middle-aged or older Caucasian males.
Facts about Chronic Leukemia
Once leukemia affects one's body, it triggers formation of faulty blood cells, causing a large number of these to enter the bloodstream. Yearly, about 29,000 adults and 2,000 children are diagnosed with leukemia in the US. The condition may be either chronic, getting worse over the course of time or acute, becoming more severe instantly. People who suffer from chronic leukemia can manage living without significant problems during the early stages of the disease. However, later, leukemia takes its toll on their well-being and, as more and more faulty cells appear in the blood, the symptoms become more serious.
Blood and Leukemia
Our blood cells are produced in the bone marrow, which is a soft tissue in the center of almost every bone in the body. Before cells become specialized for any precise function, they are called stem cells and blasts. Usually, blood cells become complete before being transferred into the bloodstream, traveling through many blood vessels in our body, to the heart.
As for leukemia cells, these are abnormal white blood cells which inhibit regular production of white and red blood cells, making it impossible for our blood to carry out its predefined tasks. This negative state of affairs may result in infections, anemia and proneness to bleeding.
The type of chronic leukemia affecting an individual depends on the type of blood cells the abnormal ones originate from. Therefore, we have chronic lymphocytic leukemia or CLL and chronic myeloid leukemia or CML. The former affects about 7,000 people yearly, most of them being older than 55. On the other hand, CML is found in 4,400 new cases of leukemia each year, mainly being found in adults as well.
Reasons behind Leukemia
Leukemia is thought to be triggered by a faulty gene in the human body, generated by a mutation. Basically, a part of one chromosome's DNA moves to another chromosome and creates the, so-called, “Philadelphia chromosome”, forcing stem cells to develop into white blood cells, even when there is no need for this. Fortunately, this chromosome cannot be transferred from a parent to a child.
Leukemia remains a mysterious medical condition which is yet incurable. Additionally, people who are at the greatest risk of suffering from leukemia are middle-aged, older Caucasian males, those who have had leukemia in their family's medical history and those who are of Russian Jew or Eastern-European Jew origin.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...