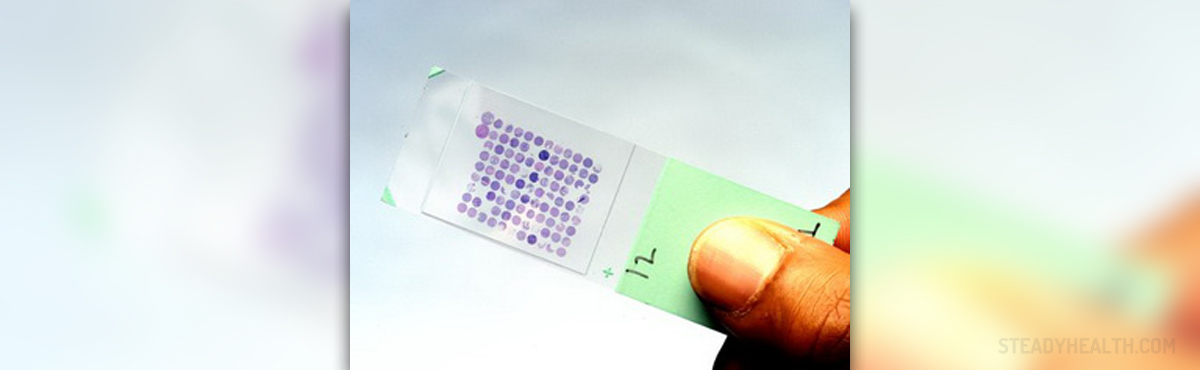
PGD or Pre-Implantation Genetic Diagnosis can be defined as genetic screening of chromosomes in an embryo prior to implantation in the uterus: this technique detects genetic abnormalities in embryos prior to implantation. This method is far more reliable than previous methods of testing. PGD are available for some time now, but these exact technologies (Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) and Microarray Analysis) are a great improvement comparing to former PGD techniques. The earliest results of these methods show a positive promise because they enable a patient an exact chromosome analysis of their embryos, which is a step forward in detecting likelihood of pregnancy and reduction in miscarriage.
Both Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) and Microarray Analysis test all 23 chromosomes in an embryo removing and testing cells from an embryo prior to implantation which is the main benefit of advanced genetic screening in fertility treatment compared to earlier Pre-Implantation Genetic Diagnosis. For example earlier PGD screening technologies only tested 9-12 chromosomes meaning they left as much as half of the chromosomes untested resulting is possibility of a chromosomal abnormality. Another benefit is the timing of testing and influence on the possibility of trauma. With the newest techniques testing is done prior to implantation which is comparing to previous PGD technique a great improvement. For example, in the past 1 or 2 cells (form 8 cells) were removed from embryo on day three of development, and this posed a high risk of trauma to the embryo. The newest techniques remove cells on day five when the embryo is consisted of over 150 cells.
- Photo courtesy of Tmalab by Flickr: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tissue_MicroArray_Slide.jpg












Your thoughts on this
Loading...