Huntington's disease is a progressive degenerative disease that affects the muscle coordination, causes death to the nerve cells in the brain and affects cognitive decline and dementia. Patients may often experience uncontrolled movements as well as the emotional and mental disturbances.
Causes
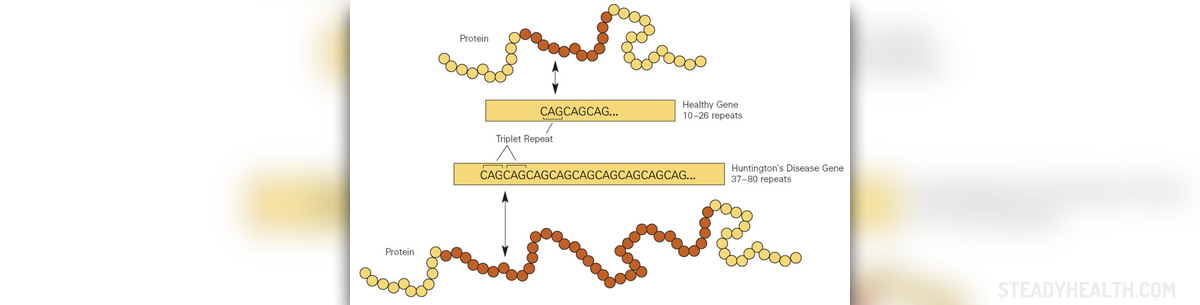
Huntington's disease occurs from genetically programmed degeneration of brain cells, called neurons, in certain areas of the brain. It is a hereditary disease, passed from parent to child through a mutation in the normal gene. The impact of a gene depends on whether it is dominant or recessive. If a gene is dominant, then only one of the paired chromosomes is necessary to produce its effect. If the gene is recessive, both parents must pass the chromosome in order to pass the inheritable feature.
Huntington's disease is called autosomal dominant disorder because only one copy of the faulty gene, inherited from only one parent, is required to generate the disease. The child has 50% of chances to inherit a disease from parent’s faulty gene. A child who inherits the Huntington's disease gene will sooner or later develop the disease, but if a child does not inherit the Huntington's disease gene, he or she will not develop the disease and cannot pass it to subsequent generations.
Symptoms
First signs of the disease are most commonly developing in the middle age. They include mood swings, irritability, apathy, passiveness, depression and anger. There are also uncontrolled movements in the fingers, feet, face, or trunk, especially when the patient is anxious. Advanced stage of the disease is defined by slurred speech and difficulty to conduct vital functions, such as swallowing, eating, speaking, and especially walking. Sometimes patients may fail to recognize their friends and family members.
Diagnosis
To set a proper diagnosis doctor will perform a physical exam, investigate about patient’s medical history as well as his or hers family medical history and question about latest emotional or intellectual changes.
If doctor suspects Huntington's disease patient will most probably undergo a psychiatric evaluation and do a blood test to determine if the abnormal gene is present or not. Patients should warn doctor if any of their parents has Huntington's disease.
Other methods doctor may suggest to help identify any changes to the brain’s structure are computerized tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
Prevention
To prevent Huntington's disease from running on further in the family, it is important to consider genetic counseling before starting a family.
Presymptomatic testing is available for people who have a family history of Huntington's disease but have no symptoms themselves. Blood tests are safe and secure way to determine the presence of the abnormal gene. If the gene is present, patients may consider adoption instead of reproduction or possibly undergo in vitro fertilization with pre-implantation screening. This procedure will screen embryos for gene mutations and implement in the woman’s uterus only those that do not have the mutation.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...