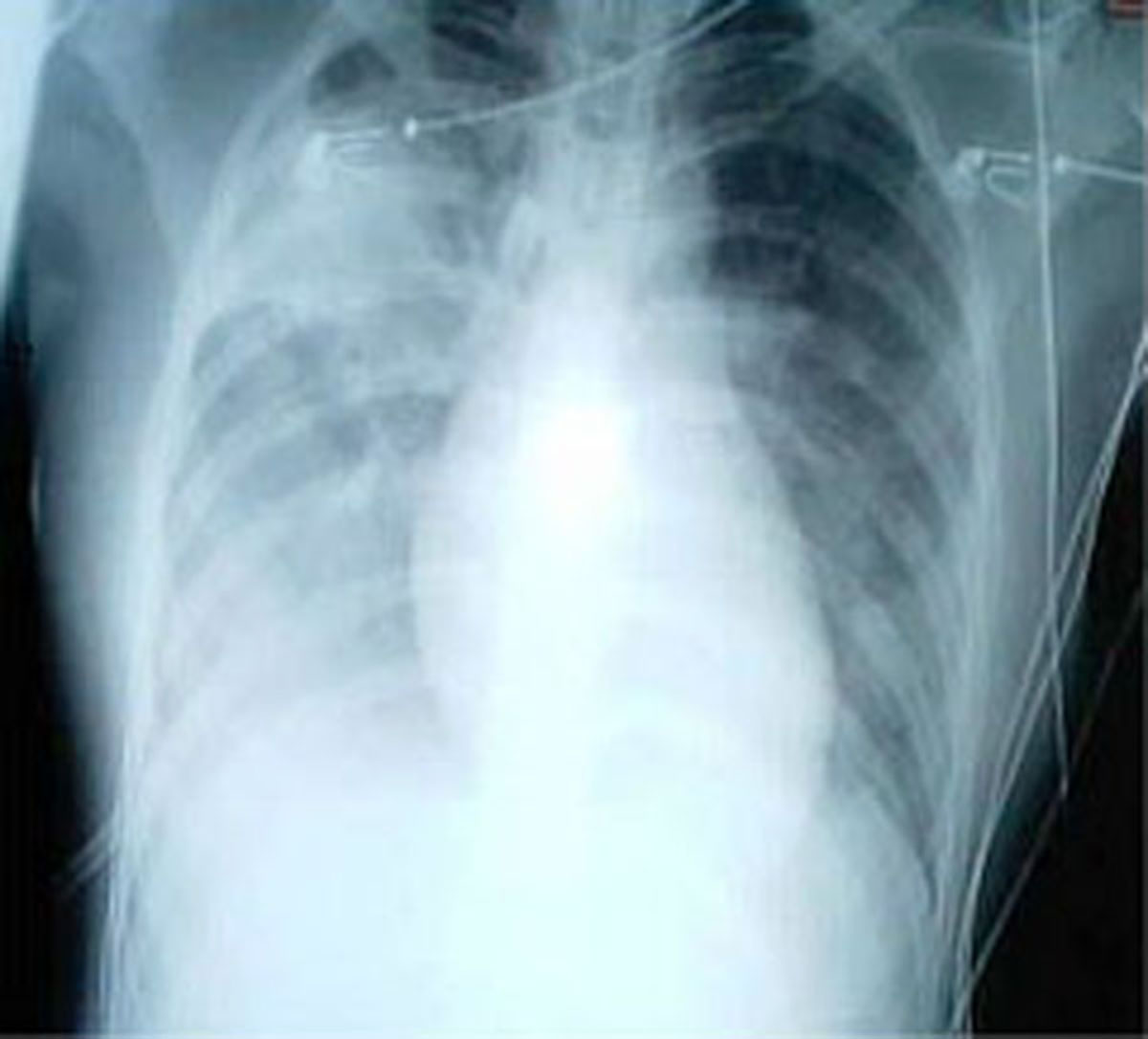
Pneumonia and fluid in the lungs
Pneumonia is a lung infection that can affect one or both lungs. The infection can be caused by a virus (including COVID-19), bacteria, or a fungus. When this occurs, the airways in the lungs, which are called alveoli and are little sacs, become inflamed and are then filled with either fluid or pus.
When the lungs are filled with fluid of pus, the lungs are not able to function properly and it can be hard to breathe, and the tissues in the body will not be getting enough oxygen.
Because of this, pneumonia can lead to serious health problems that can even be fatal in some instances.
People who have weak immune systems, such as infants, people over the age of 65, people who smoke and drink excessively, people with cancer, asthma, or AIDS, are more likely to get pneumonia.
Causes of pneumonia
A bacterial infection can cause pneumonia, as well as viruses and fungi. In the case of viral infections, frequent handwashing and staying away from (potentially) sick people can reduce your risk. During the COVID-19 pandemic, we have all become familiar with social distancing, and these same measures help reduce the spread of other viruses that can potentially lead to pneumonia as well.
An allergy such as the so-called “farmer’s lung”, in which someone is repeatedly exposed to certain molds found in crops, can also lead to pneumonia symptoms.
The inhalation of smoke and hazardous chemicals, at work or anywhere else, can also lead to the condition.
Symptoms of pneumonia
One of the most common pneumonia symptoms is a persistent and dry cough, though it later stops being dry as yellowish, as green and smelly phlegm begins to appear in the lungs.
Other symptoms of pneumonia that many patients will suffer from include fever, breathlessness, nausea, vomiting, night sweats, confusion, balance problems, a headache, chest pain or discomfort, and of course fluid in the lungs.
Fluid in the lungs in known as pleural effusion and it is often accompanied by an extreme difficulty in breathing. This often occurs when the condition of the patient continues to deteriorate and then the infection spreads to the blood and other parts of the body. The blood infection, called septicemia, is very dangerous when it occurs.
Treatment for pneumonia
In order to diagnose pneumonia and fluid in the lungs, the doctor will first look at the symptoms.
He or she will check the patient's breathing, oxygen amounts in the blood and look for the exact location of the infection and its severity, usually with an x-ray examination.
Samples of phlegm will also be examined under a microscope.
Antibiotics are should be given to treat pneumonia and its resulting fluid in the lungs when the cause is bacterial. If the patient has a very serious infection, then the patient will most likely have to go to the hospital and receive the medication through an IV.
People who are having severe problems with breathing will probably be put on a ventilator to help them get oxygen into their blood streams.
Along with the antibiotics, rest and minimal exertion is also important in order to allow the body and the antibiotics to fight off the infection.
Fungal pneumonia is treated with antifungal medications, while viral pneumonia does not have a specific cure and the patient should receive supportive care as they recover from the infection.




-And-Breathing-Problems_f_280x120.jpg)










Your thoughts on this
Loading...