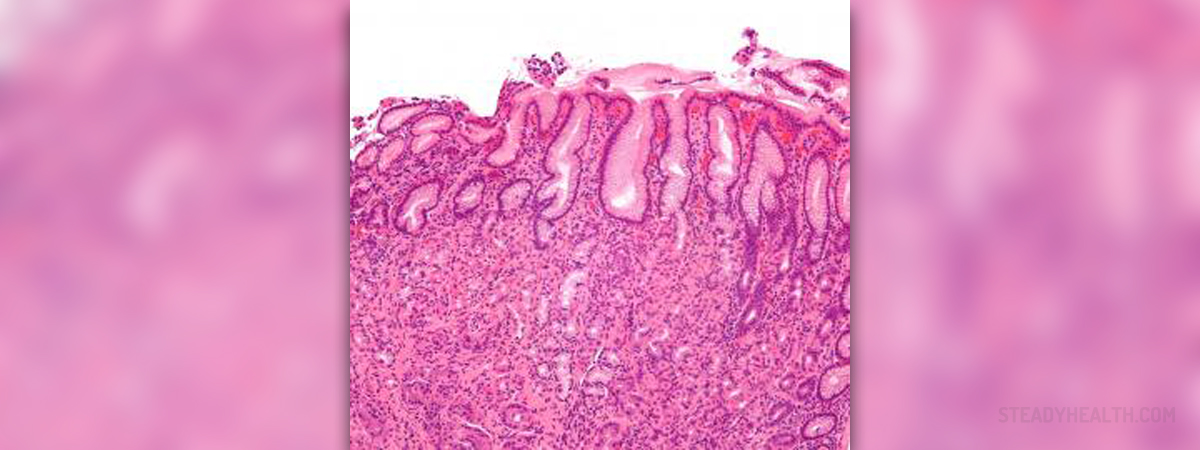
Gastritis is a medical term for inflammation of the inner surface of the stomach. Erosive gastritis is a serious inflammation of the lining of the stomach which is accompanied by the formation of ulcers on the surface of the stomach. This condition is caused by several factors and the most significant one is definitely excessive stress. Erosive gastritis may also develop as a consequence of injury, infections, autoimmune disease and prolonged intake of certain medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). Even heavy drinking may eventually result in erosive gastritis. A subtype of erosive gastritis known as acute stress gastritis develops due to a serious injury or illness such as major bleeding injuries or severe burns. These injuries can interfere with the normal circulation in the stomach and subsequently reduce its ability to produce protective substances.
Presentation of Erosive Gastritis
In erosive gastritis the mucus which is normally produced by specific cells is not synthesized in a sufficient amount, causing the lining of the stomach to not be properly protected and to be exposed to detrimental effects of stomach acid. The damage of the inner surface of the stomach if extensive and in a form of multiple, tiny ulcers, in most cases leads to bleeding.
If the condition is serious, there is usually certain symptoms and signs. Pain, being the most common sign, is located in the upper middle part of the abdomen, below the breast bone. If the lining of the stomach bleeds there may be traces of blood in the stomach content (if one is vomiting) or the blood may be mixed with the stool which gives the stool much darker color.
Additionally symptoms of erosive gastritis include indigestion/ dyspepsia, loss of appetite, nausea, bloating and belching. The symptoms and signs of erosive gastritis may be so severe that patients require immediate medical care.
Treatment for Erosive Gastritis
Initially the doctor may perform an invasive test such as gastroscopy which can visualize damage to the stomach's lining. The presence of blood can be confirmed in the stomach content and the stool.
Mild forms of erosive gastritis are treated with antacids while severe cases require acid blockers and proton pump inhibitors. In case a person is under prolonged therapy with certain medications which are responsible for erosive gastritis they need to take medications which reduce production of stomach acid the entire time of the therapy. Dietary changes are also important until the stomach lining heals properly. And finally, alcohol beverages are strictly forbidden.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...