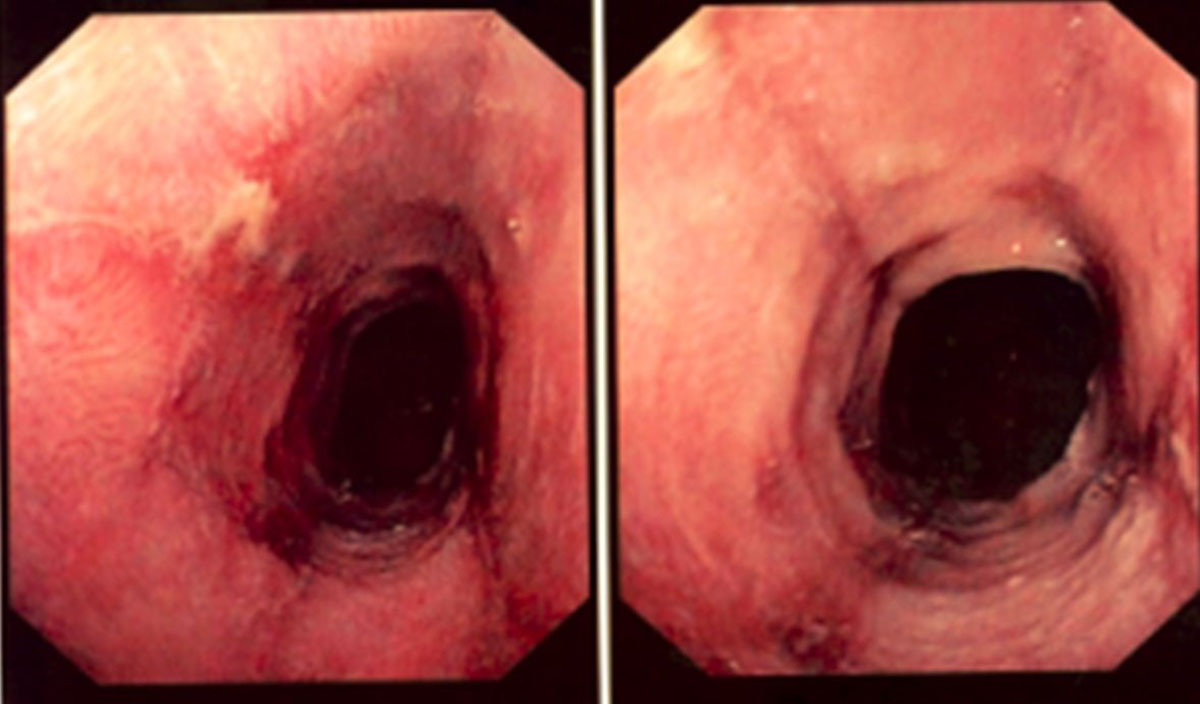
Erosive Esophagitis
Erosive esophagitis is an inflammation of the esophagus accompanied by the presence of tiny erosions of its mucous membrane.
The actual problem originates in stomach acid. Stomach or gastric acid is supposed to stay in the stomach and performs its function, start the digestion of food. However, in certain cases this acid comes up and enters the esophagus leading to its inflammation. Unlike the stomach the esophageal mucous membrane is not covered with thick layer of mucus which prevents from the direct damage of the stomach acid. This is why prolonged exposure to gastric acid eventually results in formation of esophageal erosions.
Patients who are suffering from esophagitis, either acute or chronic, have to deal with discomfort and pain. These problems especially intensity during sleep when body is in horizontal position which additionally allows stomach acid to enter the esophagus.
Symptoms of Erosive Esophagitis
The leading symptom of erosive esophagitis is heartburn. Heartburn is a burning sensation which travels from the mid chest towards the mouth. Stomach acid eventually enters the mouth and this leads to bitter taste. People may experience occasional heartburn especially after spicy and hot food. Still if this symptom occurs more than 4 times a week it may definitely point to erosive esophagitis.
Patients also complain about unpleasant feeling as if something was stuck in their throat. Additional problems are connected to swallowing which may be either difficult or even accompanied by pain. The pain is connected to inflammation and erosions and problems with swallowing develop after chronic inflammation of the esophagus when strictures have developed. In severe inflammation the esophagus may bleed. The blood can be visible in stool or in vomit. If patients are vomiting blood, it is light red and if the blood is in the stool the color of the stool becomes darker.
In extreme and neglected cases of erosive esophagitis even perforation of the esophagus is possible. It is followed by sudden, sharp pain in the chest.
Improper intake of fluids and water may consequently lead to dehydration and its symptoms.
If erosive esophagitis is not treated on time it may lead to strictures, formation of ulcers and recurrent bleeding. In some cases, chronic inflammation may even cause esophageal cancer.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Erosive Esophagitis
Definitive diagnosis can be set after endoscopic examination of the esophagus. This allows a doctor to take samples from the esophageal erosions and the diagnosis can be pathohistologically confirmed. The treatment for erosive esophagitis basically includes the treatment for hyperacidity, treatment for inflammation and in some cases complications of erosive esophagitis.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...