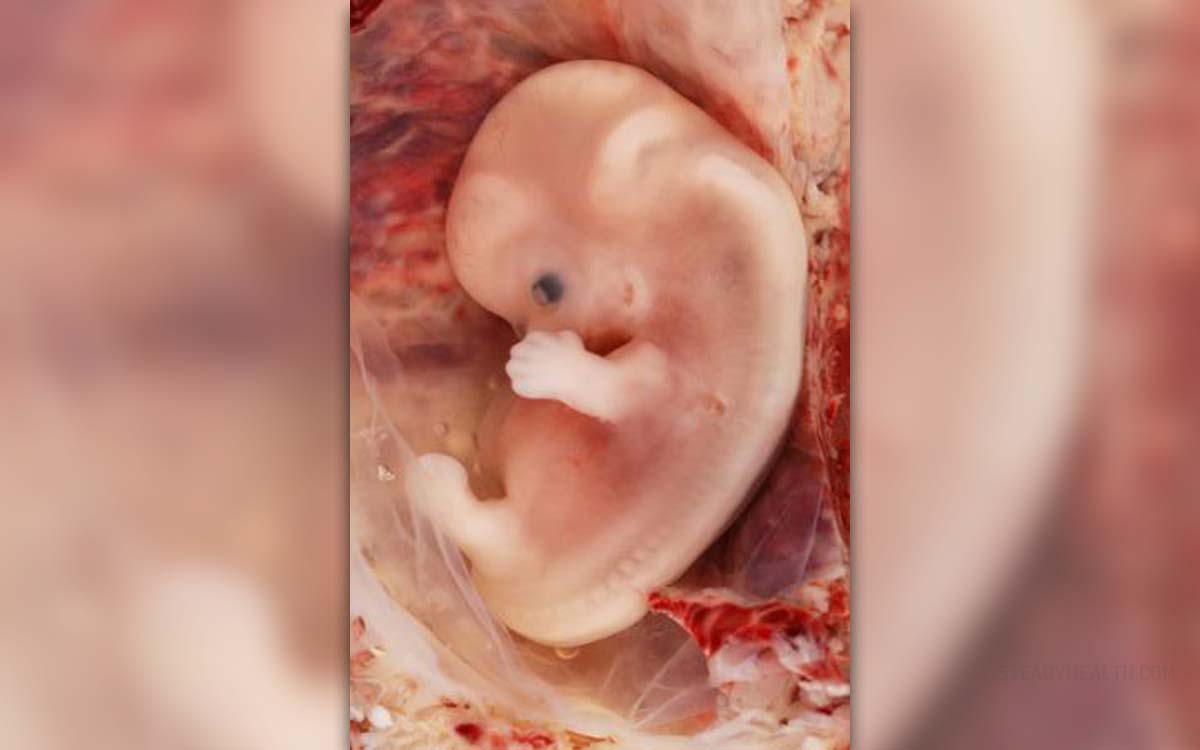
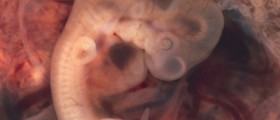
Ectopic pregnancy, also known as eccysis, is a complication of pregnancy characterized by implantation outside the uterine cavity. These pregnancies are usually not viable and present a danger for the mother’s health, as they increase the risk of internal bleeding. Most ectopic pregnancies occur in the Fallopian tube, but they are also possible in the cervix, ovaries, and abdomen. Risk factors for ectopic pregnancies include: pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, use of an intrauterine device, endometriosis, exposure to DES, tubal surgery, intrauterine surgery, smoking, previous ectopic pregnancy and tubal ligation. However, in more than one third of all cases of ectopic pregnancies, no risk factors can be identified.
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy and its Correlation with hCG
Ectopic pregnancy usually starts as a normal pregnancy and involves all of the regular symptoms such as missed menstrual period, fatigue, nausea and sore breasts. Early signs of ectopic pregnancy normally include pelvic or abdominal pain. The pain is usually sharp at one side and it gradually spreads all over the abdominal region. The pain may become worse when a woman moves. Vaginal bleeding, usually very mild, is another prominent symptom of this complication that occurs due to decreased progesterone levels. Other symptoms include pain while urinating and while having a bowel movement.
In normal pregnancy, the pregnancy hormone (hCG) doubles every 48 to 72 hours; in an ectopic pregnancy, it may climb at a lower rate or plateau. hCG is the hormone that is produced by the placenta during the pregnancy, it is detected in both urine and blood based pregnancy test. The primary role of hCG is to keep the estrogen and progesterone levels at their appropriate levels until the placenta has developed enough to take over this function.
hCG Test and ectopic pregnancy
The results of hCG tests are used to diagnose ectopic pregnancy. More than 5 mIU/ml is considered a pregnant state. Less than 5 mIU/ml is considered a non-pregnant state. However, in normal pregnancy hCG levels should increase by about 66% every 48 hours or double every 72 hours. If hCG levels are declining it may indicate that a possible miscarriage has already occurred. If hCG levels are not increasing as they should, it may indicate a pending miscarriage or a possible ectopic pregnancy. In some pregnant women, hCG levels are naturally lower and they will continue to have an otherwise normal pregnancy. Once the ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed doctors will decide on the most appropriate treatment to prevent harm to the woman. Unfortunately, ectopic pregnancy can’t be saved. For a pregnancy that has gone beyond the first few weeks, surgery is safer and more effective.








Your thoughts on this
Loading...