
Introduction
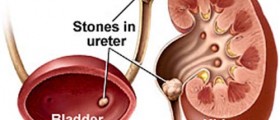
Kidney stones are the small and hard deposits that form inside of the kidneys by mineral and acid salts, though the causes are plentiful.
In the most common scenario of developing kidney stones, the urine becomes concentrated and this allows the minerals to crystallize and stick together.
When kidney stones are passed and released from the body, the process is often very painful. The pain will usually start right below the ribs and then move towards the groin area. If the stones are moving through the urinary tract, then the location of the pain will correspond to these movements.
They usually do not cause any permanent damage, and the best way to relieve the symptoms is to take regular, over-the-counter pain relieves and to drink a lot of water.
However, if they are not passed, the kidney stones can block the flow of urine, which can cause complications.
Complications
Kidney stone have been known to cause infections. An inflammation of the bladder, called cystitis, can occur if the kidney stone is blocking the urine flow from the bladder. In this case, the bladder lining is inflamed from the stone and the concentrated urine. It can lead to an infection.
If a bladder infection is not caught early, it can spread to the kidneys. Infections of the kidneys can be much more dangerous than kidney stones.
Another common complication of kidney stones is urinary retention. If the stone is blocking the urethra, then a person will not be able to urinate.
Along with the risk of contracting an infection, the bladder will also become distended and will this will cause a lot of pain.
When infections occur on a regular basis, there can be a lot of trauma on the kidney, which can cause permanent damage and lead to chronic kidney disease and chronic kidney failure, which are both very serious problems that can result from the kidney stones, which were not so serious at their onset.
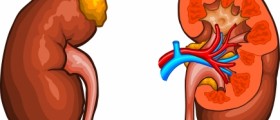
Another serious complication is acute kidney failure, in which the stone blocks the ureter and the urine cannot be drained from the kidney. The pressure inside the kidney can in this case affect the flow of blood and damage the organ. Infections are also more probable in such cases.
Treatments
Invasive treatments will be needed when the kidney stones cannot be passed naturally.
The initial treatment is usually shockwave lithotripsy, which uses high-energy sound waves that will aim to break up the stone into smaller pieces so that it will be able to be passed through urination.
If this does not work, then a surgical intervention will be the next step.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...