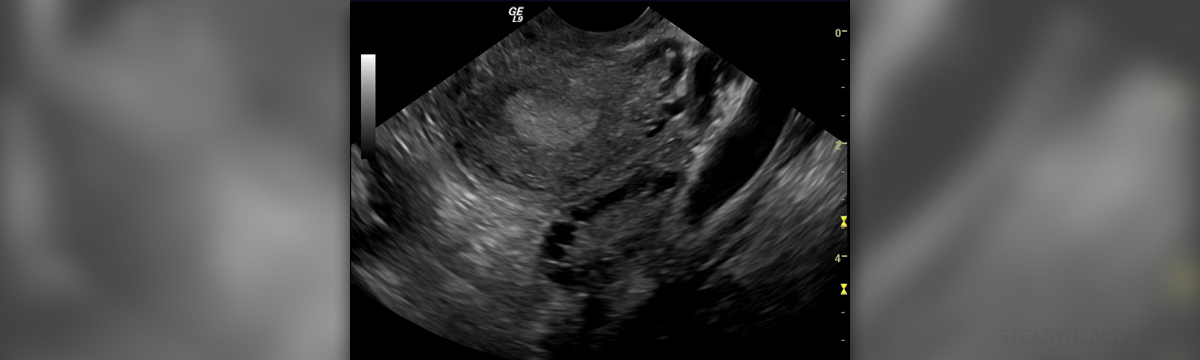
Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Polycystic ovarian syndrome is the medical term that is used for the characteristic hormonal disorder with women in their reproductive age. The women that suffer from polycystic ovarian syndrome have enlarged ovaries with many tiny cysts along the outside edge of the each ovary. Polycystic ovarian syndrome can be mild or severe, and the symptoms usually appear after the first menstruation, or later as a result of obesity, and they are different and can vary from person to person.
The woman with polycystic ovarian syndrome usually has menstruation irregularity, excessive production of androgen and polycystic ovaries. It often occurs that the woman does not have her period for several months, that her periods are lasting more than it is normal, or that she has only about eight cycles a year. With women with polycystic ovarian syndrome certain symptoms which can be seen are hirsutism or excess facial and body hair and severe adolescence acne, all this because of the excess of the male hormone androgen. In some cases even androgenic alopecia or baldness happens.
The real causes of this disorder are not precisely determined yet but there are several that can be regarded as potential. Polycystic ovarian syndrome can be inherited. Some doctors claim that the women with insulin resistance have the excess of insulin as the consequence. That excess insulin further causes the higher production of the male hormone androgen and leads to polycystic ovarian syndrome. Moreover, the women with low-grade inflammation are at risk to develop polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Complications of polycystic ovarian syndrome
The early diagnosis and proper treatment are necessary in order to avoid certain complications such as infertility and obesity. Besides that, impaired glucose tolerance or the condition commonly known as prediabetes, diabetes type 2, high blood pressure and acanthosis nigricans can also be some of the consequences of this syndrome.
Acanthosis nigricans is the medical term used for darkened skin in certain places on the body of the woman, for example, on the neck, armpits, under breasts, vulva or inner thighs. This occurs as a result of the insulin resistance. Cancer of the uterine lining, as well as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis or serious liver inflammation may appear as the consequences of untreated polycystic ovarian syndrome. Infertility usually happens because of the infrequent ovulation, or lack of ovulation. The heart diseases and stroke can be avoided if polycystic ovarian syndrome is treated on time. Furthermore, sleep apnea and abnormal uterine bleeding are also some of the complications that can be induced by polycystic ovarian syndrome.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...